Proctocolitis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
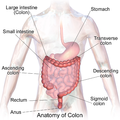
File:Blausen_0603_LargeIntestine_Anatomy.png|Anatomy of the large intestine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 22:08, 16 February 2025
Proctocolitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the rectum and the colon. It is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that primarily affects the last part of the colon, including the sigmoid colon and the rectum.
Causes
Proctocolitis can be caused by various factors, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain medications. Infections can be bacterial, viral, or parasitic. Autoimmune diseases that can cause proctocolitis include ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also cause proctocolitis.
Symptoms
The symptoms of proctocolitis can vary depending on the cause and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and weight loss. In severe cases, proctocolitis can lead to complications such as anemia, dehydration, and malnutrition.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of proctocolitis is typically made based on the patient's symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Additional tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause of the inflammation. These tests may include blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies such as colonoscopy or CT scan.
Treatment
The treatment of proctocolitis depends on the cause and severity of the inflammation. Treatment options may include antibiotics for infections, immunosuppressive drugs for autoimmune diseases, and dietary changes for certain types of proctocolitis. In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the affected part of the colon.
See also
-
Anatomy of the large intestine