Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
{{Cutaneous-condition-stub}} | {{Cutaneous-condition-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Pustular_Psoriasis.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 22:06, 16 February 2025
| Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Pustulosis of palms and soles,<ref name="Bolognia">{{{last}}},
Rapini, Ronald P., Dermatology: 2-Volume Set, St. Louis:Mosby, 2007, ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1,</ref> Palmoplantar pustulosis, Persistent palmoplantar pustulosis, Pustular psoriasis of the Barber type, and Pustular psoriasis of the extremities |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | |
| Symptoms | |
| Complications | |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | |
| Differential diagnosis | SAPHO syndrome |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | |
| Deaths | |
Alternate names
Palmoplantar pustulosis; LPP; PPP; Localized pustular psoriasis
Definition
Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris (PPP) is a rare and chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The classification of PPP is controversial. Some have proposed that PPP is a variant of psoriasis, while others believe it to be a separate disease.
Cause
- The cause of pustulosis palmaris et plantaris (PPP) is not fully understood, though many theories have been proposed. Some have suggested PPP may be a disorder of the sweat glands.
- Environmental factors are believed to play a part as well.
- For instance, there is a strong association between smoking and PPP.
- Other environmental factors that may contribute to PPP include stress, infections (especially tonsillitis and sinusitis), and certain medications. Some have also suggested an association with allergies to certain metals.
- Although most cases occur in people with no family history of the condition, more than one family member can be affected.
- This suggests that genetic factors may contribute to the development of the condition in some cases.
Signs and symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of the condition generally develop during adulthood and include crops of pustules on one or both hands and/or feet that erupt repeatedly over time.
- Affected individuals may also experience itching (pruritus), pain, or a burning sensation.
- Though the area of involvement is often limited, PPP can have a significant effect on quality of life and can interfere with walking or other daily activities.
Diagnosis
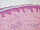
A diagnosis of pustulosis palmaris et plantaris (PPP) was made by histopathological examination that reveals hyperkeratosis with orthoheratosis, acanthosis, spongiosis and papillomatosis. A subgranular pustule, filled with polymorph nuclear neutrophils, was also observed within the epidermis. <ref>Uzun, G., Karabacak, E., Mutluoglu, M., & Aydin, E. (2013). Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris. BMJ case reports, 2013, bcr2013009400. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2013-009400</ref>.
Treatment
- Although there is no cure for pustulosis palmaris et plantaris, various measures may be useful to manage symptoms.
- General suggestions include smoking cessation and emollients (non-cosmetic moisturizers) to soften dry skin and prevent cracking.
- Topical corticosteroids (steroids), an oral retinoid such as acitretin, and photochemotherapy (ultraviolet radiation treatment) are often first-line treatments.
- Other methods that may be utilized when initial treatment options fail include a combination of oral retinoid and photochemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy with medications such as cyclosporine.
References
<references />
| Papulosquamous disorders | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|