Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Mestranol | {{Short description|Combination hormonal medication}} | ||
{{Drugbox | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002123 | |||
| image = Mestranol.svg | |||
| image2 = Hydroxyprogesterone acetate.svg | |||
| width = 200 | |||
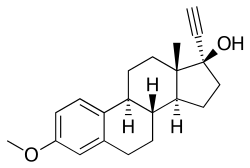
| caption = Chemical structure of Mestranol (top) and Hydroxyprogesterone acetate (bottom) | |||
}} | |||
Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate is a combination medication used for hormonal | '''Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate''' is a combination medication used in the past for hormonal therapy. It combines two active ingredients: [[mestranol]], an estrogen, and [[hydroxyprogesterone acetate]], a progestin. This combination was primarily used for [[contraception]] and [[hormone replacement therapy]]. | ||
== | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Mestranol is a prodrug of [[ethinylestradiol]], meaning it is converted into ethinylestradiol in the body. Ethinylestradiol is a potent estrogen that works by inhibiting ovulation and causing changes in the cervical mucus and endometrial lining, making it less suitable for implantation. | |||
Hydroxyprogesterone acetate is a synthetic progestin that mimics the effects of [[progesterone]]. It works by suppressing the secretion of gonadotropins from the pituitary gland, which prevents ovulation. It also induces changes in the endometrium that make it less receptive to a fertilized egg. | |||
=== | ==Medical Uses== | ||
The combination of mestranol and hydroxyprogesterone acetate was used for: | |||
* [[Contraception]]: To prevent pregnancy by inhibiting ovulation and altering the uterine lining. | |||
* [[Hormone replacement therapy]]: To alleviate symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness. | |||
==Side Effects== | |||
Common side effects of mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate include: | |||
* Nausea | |||
* Headache | |||
* Breast tenderness | |||
* Weight gain | |||
Serious side effects may include: | |||
* Increased risk of [[thrombosis]] | |||
* Hypertension | |||
* Liver dysfunction | |||
== | ==History== | ||
Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate was developed in the mid-20th century as one of the early forms of oral contraceptives. However, it has largely been replaced by newer formulations with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects. | |||
==See Also== | |||
* [[Oral contraceptive formulations]] | |||
* [[Ethinylestradiol]] | |||
* [[Progesterone]] | |||
* [[Hormone replacement therapy]] | |||
== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Combined hormonal contraceptives]] | |||
[[Category:Estrogens]] | |||
[[Category:Progestogens]] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:00, 11 December 2024
Combination hormonal medication
| Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate is a combination medication used in the past for hormonal therapy. It combines two active ingredients: mestranol, an estrogen, and hydroxyprogesterone acetate, a progestin. This combination was primarily used for contraception and hormone replacement therapy.
Pharmacology[edit]
Mestranol is a prodrug of ethinylestradiol, meaning it is converted into ethinylestradiol in the body. Ethinylestradiol is a potent estrogen that works by inhibiting ovulation and causing changes in the cervical mucus and endometrial lining, making it less suitable for implantation.
Hydroxyprogesterone acetate is a synthetic progestin that mimics the effects of progesterone. It works by suppressing the secretion of gonadotropins from the pituitary gland, which prevents ovulation. It also induces changes in the endometrium that make it less receptive to a fertilized egg.
Medical Uses[edit]
The combination of mestranol and hydroxyprogesterone acetate was used for:
- Contraception: To prevent pregnancy by inhibiting ovulation and altering the uterine lining.
- Hormone replacement therapy: To alleviate symptoms of menopause such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate include:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Breast tenderness
- Weight gain
Serious side effects may include:
- Increased risk of thrombosis
- Hypertension
- Liver dysfunction
History[edit]
Mestranol/hydroxyprogesterone acetate was developed in the mid-20th century as one of the early forms of oral contraceptives. However, it has largely been replaced by newer formulations with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>