Nabumetone: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
{{nsaids}} | {{nsaids}} | ||
{{coststubd}} | {{coststubd}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
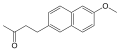
File:Nabumetone.svg|Nabumetone | |||
File:Nabumetone Metabolism.gif|Nabumetone Metabolism | |||
</gallery> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Nabumetone.svg|Nabumetone | File:Nabumetone.svg|Nabumetone | ||
File:Nabumetone Metabolism.gif|Nabumetone Metabolism | File:Nabumetone Metabolism.gif|Nabumetone Metabolism | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 01:45, 20 February 2025
Information about Nabumetone
Nabumetone is a long acting nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) that is available by prescription only and is used in therapy of chronic arthritis.
Liver safety of Nabumetone
Nabumetone has been linked to rare instances of clinically apparent, idiosyncratic drug induced liver disease.
Mechanism of action of Nabumetone
Nabumetone (nab ue' me tone) is a naphthyl alkanone and orally available antiinflammatory agent. Like other NSAIDs, nabumetone is a potent cyclo-oxygenase (Cox-1 and -2) inhibitor, which blocks the formation of prostaglandins that are important mediators in pain and inflammatory pathways. Nabumetone is a pro-drug and exerts anti-cyclo-oxygenase activity only after absorption and activation in the liver. Like other NSAIDs, it has analgesic, antipyretic and antiinflammatory activities.
FDA approval information for Nabumetone
Nabumetone was approved in the United States in 1991 and its current indications are for treatment of chronic arthritis due to osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Nabumetone is available by prescription only, and currently more than 4 million prescriptions are filled yearly. Generic formulations are available of 500 and 750 mg; specific commercially available names include Relafen (500 mg). The usual dose in adults is 1000 mg once daily, increasing to as much as 2000 mg daily based upon response and tolerance.
{se}} As with other NSAIDs, nabumetone is generally well tolerated, but side effects can included headache, dizziness, somnolence, dyspepsia, nausea, abdominal discomfort, heartburn, peripheral edema and hypersensitivity reactions.
Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Acetaminophen, Celecoxib, Diclofenac, Diflunisal, Etodolac, Fenoprofen, Flurbiprofen, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin, Ketoprofen, Ketorolac, Mefenamic Acid, Meloxicam, Nabumetone, Naproxen, Nimesulide, Oxaprozin, Phenylbutazone, Piroxicam, Rofecoxib, Sulindac, Tolmetin
-
Nabumetone
-
Nabumetone Metabolism
-
Nabumetone
-
Nabumetone Metabolism