Malathion: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
File:Malathion.png|Malathion | File:Malathion.png|Malathion | ||
Latest revision as of 00:40, 17 March 2025
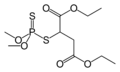
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide that is commonly used in agriculture, residential landscaping, public recreation areas, and in public health pest control programs such as mosquito eradication. It is produced by the addition of a thio group to diethyl malonate. The compound is chiral but is used as a racemate.
Chemistry[edit]
Malathion is a derivative of malonic acid. It is synthesized by adding a thio group to diethyl malonate. The compound is chiral, meaning it has two non-superimposable mirror images. However, it is used as a racemate, a 1:1 mixture of the two forms.
Uses[edit]
Malathion is primarily used as an insecticide in the agricultural sector to control insects on fruit, vegetables, and other crops. It is also used in residential landscaping, public recreation areas, and in public health pest control programs such as mosquito eradication.
Health effects[edit]
Exposure to malathion can cause a variety of health effects, depending on the amount and duration of exposure. These can range from minor symptoms such as headache and nausea, to more serious effects such as seizures and even death in severe cases. Malathion is also a potential carcinogen.
Environmental impact[edit]
Malathion can have a significant impact on the environment. It is highly toxic to aquatic life and can cause harm to non-target organisms. It also has the potential to contaminate water sources.
Regulation[edit]
In many countries, the use of malathion is regulated by government agencies. These regulations often include restrictions on its use, as well as requirements for its safe storage and disposal.