Aliasing: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
File:Aliasing.gif|Aliasing | File:Aliasing.gif|Aliasing | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Aliasing == | |||
Aliasing is a phenomenon that occurs in signal processing and related fields, where different continuous signals become indistinguishable (or aliases of one another) when sampled. It is a critical concept in the fields of [[digital signal processing]], [[image processing]], and [[computer graphics]]. | |||
=== Signal Processing === | |||
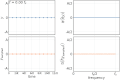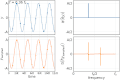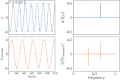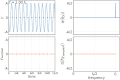
In the context of [[signal processing]], aliasing refers to the distortion that occurs when a signal is undersampled. According to the [[Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem]], a continuous signal can be completely represented by its samples and fully reconstructed if it is sampled at a rate greater than twice its highest frequency component. This rate is known as the [[Nyquist rate]]. | |||
If a signal is sampled below the Nyquist rate, higher frequency components of the signal can be misrepresented as lower frequency components, leading to aliasing. This can result in a loss of information and distortion in the reconstructed signal. | |||
=== Image Processing === | |||
In [[image processing]], aliasing manifests as jagged edges or "jaggies" in digital images. This occurs when high-frequency detail in the image is not adequately sampled, leading to visual artifacts. Techniques such as [[anti-aliasing]] are used to reduce these effects by smoothing out the edges. | |||
=== Computer Graphics === | |||
In [[computer graphics]], aliasing can occur when rendering images, particularly when representing high-frequency textures or fine details. Anti-aliasing techniques are employed to minimize the visual impact of aliasing by averaging colors at the boundaries of objects to create a smoother transition. | |||
=== Audio Processing === | |||
In [[audio processing]], aliasing can cause high-frequency sounds to be misrepresented as lower frequencies, leading to distortion. This is particularly problematic in digital audio systems where the sampling rate is not sufficiently high to capture all the nuances of the sound. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem]] | |||
* [[Digital signal processing]] | |||
* [[Anti-aliasing]] | |||
* [[Image processing]] | |||
* [[Computer graphics]] | |||
{{Signal processing}} | |||
{{Image processing}} | |||
[[Category:Signal processing]] | |||
[[Category:Image processing]] | |||
[[Category:Computer graphics]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:35, 19 February 2025
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
-
Aliasing
Aliasing[edit]
Aliasing is a phenomenon that occurs in signal processing and related fields, where different continuous signals become indistinguishable (or aliases of one another) when sampled. It is a critical concept in the fields of digital signal processing, image processing, and computer graphics.
Signal Processing[edit]
In the context of signal processing, aliasing refers to the distortion that occurs when a signal is undersampled. According to the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, a continuous signal can be completely represented by its samples and fully reconstructed if it is sampled at a rate greater than twice its highest frequency component. This rate is known as the Nyquist rate.
If a signal is sampled below the Nyquist rate, higher frequency components of the signal can be misrepresented as lower frequency components, leading to aliasing. This can result in a loss of information and distortion in the reconstructed signal.
Image Processing[edit]
In image processing, aliasing manifests as jagged edges or "jaggies" in digital images. This occurs when high-frequency detail in the image is not adequately sampled, leading to visual artifacts. Techniques such as anti-aliasing are used to reduce these effects by smoothing out the edges.
Computer Graphics[edit]
In computer graphics, aliasing can occur when rendering images, particularly when representing high-frequency textures or fine details. Anti-aliasing techniques are employed to minimize the visual impact of aliasing by averaging colors at the boundaries of objects to create a smoother transition.
Audio Processing[edit]
In audio processing, aliasing can cause high-frequency sounds to be misrepresented as lower frequencies, leading to distortion. This is particularly problematic in digital audio systems where the sampling rate is not sufficiently high to capture all the nuances of the sound.
Related Pages[edit]
- Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
- Digital signal processing
- Anti-aliasing
- Image processing
- Computer graphics
| Signal processing | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This signal processing related article is a stub.
|