Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm | |||
| image = [[File:IPMN_T2w_ax-07_a.jpg]] | |||
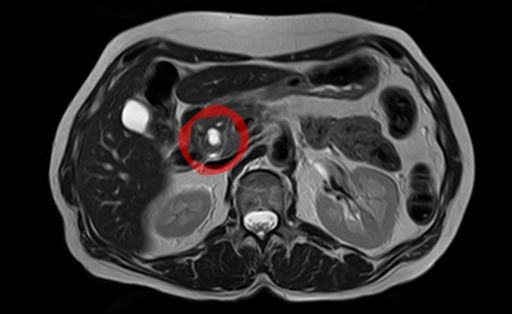
| caption = MRI image of an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm | |||
| field = [[Gastroenterology]], [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = IPMN | |||
| symptoms = [[Abdominal pain]], [[jaundice]], [[pancreatitis]] | |||
| complications = [[Pancreatic cancer]], [[diabetes mellitus]] | |||
| onset = Typically in [[middle age]] to [[elderly]] | |||
| duration = Chronic | |||
| types = Main duct, branch duct, mixed type | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = [[Smoking]], [[chronic pancreatitis]], [[genetic predisposition]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], [[Endoscopic ultrasound|EUS]], [[CT scan]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Pancreatic cyst]], [[mucinous cystic neoplasm]], [[serous cystadenoma]] | |||
| prevention = Regular monitoring, lifestyle changes | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical resection]], [[surveillance]] | |||
| medication = None specific | |||
| prognosis = Varies; risk of malignancy | |||
| frequency = Increasing with age | |||
| deaths = Related to progression to cancer | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Histopathology_of_intraductal_papillary_mucinous_neoplasm_types.jpg|Histopathology of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm types|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Relative_incidence_of_pancreatic_neoplasms.png|Relative incidence of pancreatic neoplasms|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm''' ('''IPMN''') is a type of [[pancreatic cyst]] that can develop into [[pancreatic cancer]]. It is characterized by the growth of mucus-producing cells in the pancreatic ducts. | '''Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm''' ('''IPMN''') is a type of [[pancreatic cyst]] that can develop into [[pancreatic cancer]]. It is characterized by the growth of mucus-producing cells in the pancreatic ducts. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | |||
IPMN is a [[precancerous lesion]] that arises from the [[pancreas]], a vital organ that plays essential roles in digestion and hormone production. The pancreas is composed of exocrine and endocrine cells. The exocrine cells produce enzymes that aid in digestion, while the endocrine cells produce hormones like insulin. In IPMN, the exocrine cells, specifically those lining the pancreatic ducts, start to proliferate abnormally, leading to the formation of cysts filled with mucus. | IPMN is a [[precancerous lesion]] that arises from the [[pancreas]], a vital organ that plays essential roles in digestion and hormone production. The pancreas is composed of exocrine and endocrine cells. The exocrine cells produce enzymes that aid in digestion, while the endocrine cells produce hormones like insulin. In IPMN, the exocrine cells, specifically those lining the pancreatic ducts, start to proliferate abnormally, leading to the formation of cysts filled with mucus. | ||
==Types== | ==Types== | ||
There are two main types of IPMN: main duct IPMN and branch duct IPMN. [[Main duct IPMN]] involves the main pancreatic duct, while [[branch duct IPMN]] involves the smaller side branches. Main duct IPMN is more likely to progress to cancer than branch duct IPMN. | There are two main types of IPMN: main duct IPMN and branch duct IPMN. [[Main duct IPMN]] involves the main pancreatic duct, while [[branch duct IPMN]] involves the smaller side branches. Main duct IPMN is more likely to progress to cancer than branch duct IPMN. | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of IPMN can vary and often depend on the location and size of the cysts. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and jaundice. However, many people with IPMN do not have any symptoms, and the condition is often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions. | Symptoms of IPMN can vary and often depend on the location and size of the cysts. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and jaundice. However, many people with IPMN do not have any symptoms, and the condition is often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of IPMN typically involves imaging tests such as [[computed tomography (CT) scan]], [[magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)]], and [[endoscopic ultrasound]]. In some cases, a sample of the cyst fluid may be taken for analysis, a procedure known as [[fine-needle aspiration]]. | Diagnosis of IPMN typically involves imaging tests such as [[computed tomography (CT) scan]], [[magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)]], and [[endoscopic ultrasound]]. In some cases, a sample of the cyst fluid may be taken for analysis, a procedure known as [[fine-needle aspiration]]. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The treatment for IPMN depends on several factors, including the type of IPMN, the size of the cysts, the presence of symptoms, and the overall health of the patient. Options may include surveillance, surgical removal of the cysts, or total pancreatectomy in severe cases. | The treatment for IPMN depends on several factors, including the type of IPMN, the size of the cysts, the presence of symptoms, and the overall health of the patient. Options may include surveillance, surgical removal of the cysts, or total pancreatectomy in severe cases. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for IPMN varies depending on the type and stage of the disease. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis. | The prognosis for IPMN varies depending on the type and stage of the disease. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis. | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Pancreatic diseases]] | [[Category:Pancreatic diseases]] | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:19, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | IPMN |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, jaundice, pancreatitis |
| Complications | Pancreatic cancer, diabetes mellitus |
| Onset | Typically in middle age to elderly |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | Main duct, branch duct, mixed type |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Smoking, chronic pancreatitis, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | MRI, EUS, CT scan, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Pancreatic cyst, mucinous cystic neoplasm, serous cystadenoma |
| Prevention | Regular monitoring, lifestyle changes |
| Treatment | Surgical resection, surveillance |
| Medication | None specific |
| Prognosis | Varies; risk of malignancy |
| Frequency | Increasing with age |
| Deaths | Related to progression to cancer |


Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a type of pancreatic cyst that can develop into pancreatic cancer. It is characterized by the growth of mucus-producing cells in the pancreatic ducts.
Introduction[edit]
IPMN is a precancerous lesion that arises from the pancreas, a vital organ that plays essential roles in digestion and hormone production. The pancreas is composed of exocrine and endocrine cells. The exocrine cells produce enzymes that aid in digestion, while the endocrine cells produce hormones like insulin. In IPMN, the exocrine cells, specifically those lining the pancreatic ducts, start to proliferate abnormally, leading to the formation of cysts filled with mucus.
Types[edit]
There are two main types of IPMN: main duct IPMN and branch duct IPMN. Main duct IPMN involves the main pancreatic duct, while branch duct IPMN involves the smaller side branches. Main duct IPMN is more likely to progress to cancer than branch duct IPMN.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of IPMN can vary and often depend on the location and size of the cysts. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and jaundice. However, many people with IPMN do not have any symptoms, and the condition is often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of IPMN typically involves imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and endoscopic ultrasound. In some cases, a sample of the cyst fluid may be taken for analysis, a procedure known as fine-needle aspiration.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for IPMN depends on several factors, including the type of IPMN, the size of the cysts, the presence of symptoms, and the overall health of the patient. Options may include surveillance, surgical removal of the cysts, or total pancreatectomy in severe cases.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for IPMN varies depending on the type and stage of the disease. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
