Pudendal nerve entrapment: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} {{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Pudendal nerve entrapment | |||
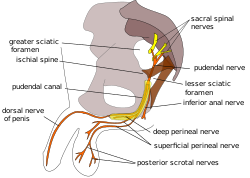
| image = [[File:Pudendal_nerve.svg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Diagram of the [[pudendal nerve]] | |||
| synonyms = Alcock canal syndrome, pudendal neuralgia | |||
| specialty = [[Neurology]], [[Urology]], [[Gynecology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Chronic pain]] in the [[pelvis]], [[genital]]s, or [[perineum]] | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Long-term | |||
| causes = [[Compression]] of the [[pudendal nerve]] | |||
| risks = [[Cycling]], [[childbirth]], [[pelvic surgery]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical examination]], [[nerve conduction study]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Interstitial cystitis]], [[prostatitis]], [[vulvodynia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Physical therapy]], [[nerve block]], [[surgery]] | |||
| medication = [[Pain management]], [[anticonvulsants]], [[antidepressants]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, can be managed with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
[[File:CT_image_guided_injection_pudendal_nerve.png|CT image guided injection of the pudendal nerve|thumb|left]] | |||
'''Pudendal nerve entrapment''' (PNE), also known as '''Alcock canal syndrome''', is a condition that results in chronic pelvic pain. The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If this nerve is damaged or compressed, it can cause pain, discomfort or numbness in these areas. | '''Pudendal nerve entrapment''' (PNE), also known as '''Alcock canal syndrome''', is a condition that results in chronic pelvic pain. The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If this nerve is damaged or compressed, it can cause pain, discomfort or numbness in these areas. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Pudendal nerve entrapment can be caused by a variety of factors. These include [[pregnancy]], [[surgery]], [[cycling]], [[squatting exercises]], and [[trauma]] to the area. In some cases, the cause of PNE is unknown. | Pudendal nerve entrapment can be caused by a variety of factors. These include [[pregnancy]], [[surgery]], [[cycling]], [[squatting exercises]], and [[trauma]] to the area. In some cases, the cause of PNE is unknown. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
The symptoms of pudendal nerve entrapment can vary greatly from person to person. They may include: | The symptoms of pudendal nerve entrapment can vary greatly from person to person. They may include: | ||
* [[Pain]] in the perineum, genitals, or rectum | * [[Pain]] in the perineum, genitals, or rectum | ||
* [[Numbness]] or [[tingling]] in these areas | * [[Numbness]] or [[tingling]] in these areas | ||
| Line 12: | Line 28: | ||
* [[Urinary incontinence]] or [[fecal incontinence]] | * [[Urinary incontinence]] or [[fecal incontinence]] | ||
* [[Constipation]] | * [[Constipation]] | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of pudendal nerve entrapment can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. Diagnostic tests may include a [[nerve conduction study]], [[MRI]], or [[CT scan]]. In some cases, a [[pudendal nerve block]] may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. | Diagnosis of pudendal nerve entrapment can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. Diagnostic tests may include a [[nerve conduction study]], [[MRI]], or [[CT scan]]. In some cases, a [[pudendal nerve block]] may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment for pudendal nerve entrapment can include a variety of options, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause of the condition. These may include: | Treatment for pudendal nerve entrapment can include a variety of options, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause of the condition. These may include: | ||
* [[Physical therapy]] | * [[Physical therapy]] | ||
* [[Medications]] to manage pain | * [[Medications]] to manage pain | ||
* [[Nerve block injections]] | * [[Nerve block injections]] | ||
* [[Surgery]] | * [[Surgery]] | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Pelvic pain]] | * [[Pelvic pain]] | ||
* [[Pudendal nerve]] | * [[Pudendal nerve]] | ||
* [[Pudendal nerve block]] | * [[Pudendal nerve block]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Nervous system disorders]] | [[Category:Nervous system disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Pain]] | [[Category:Pain]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:11, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Pudendal nerve entrapment | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Alcock canal syndrome, pudendal neuralgia |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Neurology, Urology, Gynecology |
| Symptoms | Chronic pain in the pelvis, genitals, or perineum |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Compression of the pudendal nerve |
| Risks | Cycling, childbirth, pelvic surgery |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, nerve conduction study, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Interstitial cystitis, prostatitis, vulvodynia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, nerve block, surgery |
| Medication | Pain management, anticonvulsants, antidepressants |
| Prognosis | Variable, can be managed with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |

Pudendal nerve entrapment (PNE), also known as Alcock canal syndrome, is a condition that results in chronic pelvic pain. The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If this nerve is damaged or compressed, it can cause pain, discomfort or numbness in these areas.
Causes[edit]
Pudendal nerve entrapment can be caused by a variety of factors. These include pregnancy, surgery, cycling, squatting exercises, and trauma to the area. In some cases, the cause of PNE is unknown.
Symptoms[edit]
The symptoms of pudendal nerve entrapment can vary greatly from person to person. They may include:
- Pain in the perineum, genitals, or rectum
- Numbness or tingling in these areas
- Sexual dysfunction
- Urinary incontinence or fecal incontinence
- Constipation
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of pudendal nerve entrapment can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential. Diagnostic tests may include a nerve conduction study, MRI, or CT scan. In some cases, a pudendal nerve block may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for pudendal nerve entrapment can include a variety of options, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause of the condition. These may include:
- Physical therapy
- Medications to manage pain
- Nerve block injections
- Surgery
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />


