1,4-Dioxin: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[[Category:Heterocyclic compounds]] | [[Category:Heterocyclic compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Organic chemistry]] | [[Category:Organic chemistry]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:1,4-Dioxin.svg|1,4-Dioxin | |||
File:Synthesis-of-1,4-dioxin-1994-2D-skeletal.png|Synthesis of 1,4-Dioxin (1994) | |||
File:Dibenzo-p-dioxin-numbering-2D-skeletal.png|Dibenzo-p-dioxin numbering | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 03:52, 18 February 2025
1,4-Dioxin[edit]

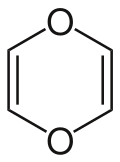
1,4-Dioxin is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C_H_O_. It is a six-membered ring containing two oxygen atoms opposite each other in the ring. This compound is of interest in organic chemistry due to its unique structure and reactivity.
Structure and Properties[edit]
1,4-Dioxin is characterized by a six-membered ring structure with alternating single and double bonds, making it an example of a heterocyclic compound. The presence of two oxygen atoms in the ring contributes to its chemical properties, including its ability to participate in various chemical reactions.
The compound is typically depicted in its resonance forms, which illustrate the delocalization of electrons across the ring. This delocalization imparts some degree of stability to the molecule, although it is generally less stable than its isomer, 1,3-dioxin.
Synthesis[edit]
1,4-Dioxin can be synthesized through several methods, often involving the cyclization of appropriate precursors. One common method involves the reaction of ethylene glycol with glyoxal in the presence of an acid catalyst. This reaction forms the dioxin ring through a dehydration process.
Chemical Reactions[edit]
1,4-Dioxin is reactive due to the presence of the oxygen atoms and the unsaturated nature of the ring. It can undergo various chemical transformations, including oxidation, reduction, and nucleophilic substitution reactions. These reactions are often used to modify the dioxin ring for further chemical synthesis.
Applications[edit]
While 1,4-Dioxin itself is not widely used in industry, its derivatives and related compounds are important in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. The study of 1,4-Dioxin and its reactions provides valuable insights into the behavior of heterocyclic compounds in organic chemistry.
Related Compounds[edit]
1,4-Dioxin is related to other dioxin compounds, such as 1,3-dioxin and dibenzo-p-dioxin. These compounds share similar structural features but differ in the position of the oxygen atoms and the nature of the ring system.
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Structure of 1,4-Dioxin
-
Synthesis of 1,4-Dioxin
-
Dibenzo-p-dioxin structure
-
1,4-Dioxin
-
Synthesis of 1,4-Dioxin (1994)
-
Dibenzo-p-dioxin numbering