Thiophosphate: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
{{Chemistry-stub}} | {{Chemistry-stub}} | ||
==Thiophosphate== | |||
<gallery> | |||
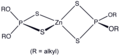
File:Zn(dtp)2.png|Zinc diethyldithiophosphate | |||
File:RS_Phosphorothioates.svg|Phosphorothioate structure | |||
File:Amifostine.svg|Amifostine chemical structure | |||
File:Chlorpyrifos.svg|Chlorpyrifos chemical structure | |||
File:Malathion.png|Malathion chemical structure | |||
File:ThiophosphateVarietyPack.png|Thiophosphate variety pack | |||
File:Thiophosphate-ion-3D-balls.png|Thiophosphate ion 3D model | |||
File:PS3-dimerization.png|PS3 dimerization | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 18 February 2025
Thiophosphate compounds are a class of phosphorus-containing chemical compounds where one or more of the oxygen atoms bonded to phosphorus are replaced by sulfur atoms. These compounds are considered derivatives of the phosphate ion (PO43-) and can exist in several forms, including mono-, di-, and tri-thiophosphates, depending on the number of sulfur atoms replacing oxygen atoms. Thiophosphates have diverse applications in agriculture, medicine, and industry, serving as pesticides, flame retardants, and antioxidants, among other uses.
Chemistry and Synthesis[edit]
Thiophosphate compounds are synthesized through the process of thionation, which involves the substitution of oxygen atoms in phosphate compounds with sulfur. This can be achieved using various reagents such as phosphorus pentasulfide (P2S5) or thiophosphoryl chloride (PSCl3). The general reaction can be represented as follows:
PO43- + S → PSO32- + O
The chemistry of thiophosphates is characterized by their reactivity and the ability to form various derivatives, including salts and esters. The presence of sulfur atoms in these compounds often imparts unique physical and chemical properties compared to their oxygen-only counterparts.
Applications[edit]
Agriculture[edit]
In agriculture, thiophosphate compounds are widely used as insecticides and fungicides due to their ability to inhibit certain enzymes critical to pests. Examples include malathion and parathion, which are organophosphorus insecticides derived from thiophosphate.
Medicine[edit]
In the medical field, certain thiophosphate derivatives serve as drugs and biomolecules. For instance, thiophosphate analogs of nucleotides are used in research and therapeutic applications, including the treatment of viral infections and cancer.
Industry[edit]
Industrially, thiophosphates find applications as additives in lubricants and hydraulic fluids to improve anti-wear and antioxidant properties. They are also used in the manufacture of plastics and rubbers as flame retardants.
Safety and Environmental Concerns[edit]
The use of thiophosphate compounds, especially in agriculture and pest control, raises concerns regarding their toxicity to humans and wildlife. Many organophosphorus pesticides are potent neurotoxins, and their persistence in the environment can lead to contamination of water sources and food chains. Regulatory measures and safety guidelines are in place to manage the risks associated with these chemicals.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>
Thiophosphate[edit]
-
Zinc diethyldithiophosphate
-
Phosphorothioate structure
-
Amifostine chemical structure
-
Chlorpyrifos chemical structure
-
Malathion chemical structure
-
Thiophosphate variety pack
-
Thiophosphate ion 3D model
-
PS3 dimerization