Phenazine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
==Phenazine== | |||
<gallery> | |||
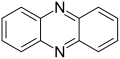
File:Phenazine_200.svg|Phenazine chemical structure | |||
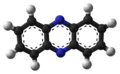
File:Phenazine-3D-balls-B.png|3D ball model of Phenazine | |||
File:Ru(phen)2(dppz)2+.svg|Ruthenium complex with phenazine | |||
File:Neutral_red.png|Neutral red dye | |||
File:Pyocyanin_Biosynthesis.png|Pyocyanin biosynthesis pathway | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:49, 18 February 2025
Phenazine is a dyeing agent and antibiotic compound that is derived from bacterial sources. It is a heterocyclic compound, specifically a diazine, with the molecular formula C12H8N2.
History[edit]
Phenazine was first isolated in 1834 by the French chemist Auguste Laurent. It was later synthesized in the laboratory by the German chemist Karl Graebe in 1882.
Structure and Properties[edit]
Phenazine is a planar molecule that consists of three benzene rings fused together with two nitrogen atoms replacing carbon at the 1,10-positions. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and chloroform.
Biological Role[edit]
Phenazine compounds are produced by several species of bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptomyces. They play a role in the bacterial biofilm formation and are involved in the bacterial quorum sensing mechanism. Some phenazine derivatives have antibiotic properties and are being investigated for their potential use in medical applications.
Synthesis[edit]
Phenazine can be synthesized in the laboratory by several methods, including the Graebe-Ullmann synthesis, which involves the condensation of aniline with glyoxal under acidic conditions.
Applications[edit]
Phenazine and its derivatives have been used as dyes, pigments, and fluorescent probes. They are also being investigated for their potential use in organic electronics and as antibiotics.
Safety[edit]
Phenazine is not considered highly toxic, but it can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. It should be handled with care using appropriate safety equipment.
See Also[edit]
Phenazine[edit]
-
Phenazine chemical structure
-
3D ball model of Phenazine
-
Ruthenium complex with phenazine
-
Neutral red dye
-
Pyocyanin biosynthesis pathway