Spermatocyte: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Figure_28_01_04.jpg|Spermatocyte | |||
File:Mitosis_(263_06)_Grasshopper_testes_(Spermatogonia).jpg|Grasshopper testes (Spermatogonia) | |||
File:Spermatocytogenesis.png|Spermatocytogenesis | |||
File:1810_Major_Pituitary_Hormones.jpg|Spermatocyte | |||
File:Repro4_mutation_in_Spermatocytes.jpg|Mutation in Spermatocytes | |||
File:Meiosis_(248_23).jpg|Meiosis | |||
File:Mesostoma_ehrenbergii.jpg|Spermatocyte | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:18, 18 February 2025
Spermatocyte
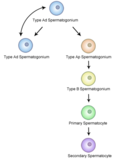
A Spermatocyte is a male gametocyte, derived from a spermatogonium, which is in the process of developing into a spermatozoon. This process is known as spermatogenesis.
Overview[edit]
Spermatocytes are found in the testis, specifically in the seminiferous tubules. They are a crucial part of the male reproductive system, as they are the cells that undergo meiosis to ultimately form spermatozoa.
Development[edit]
The development of a spermatocyte involves several stages. Initially, a spermatogonium undergoes mitosis to form two spermatogonia. One of these remains as a spermatogonium, while the other differentiates into a primary spermatocyte.
Primary Spermatocytes[edit]
A primary spermatocyte is a type of spermatocyte that undergoes the first division of meiosis (Meiosis I). This division is a reductional division because the primary spermatocyte is diploid (2n) and the secondary spermatocytes are haploid (n).
Secondary Spermatocytes[edit]
Secondary spermatocytes are the result of the first meiotic division of the primary spermatocyte. Each primary spermatocyte produces two secondary spermatocytes, which then undergo the second division of meiosis (Meiosis II) to produce spermatids.
Function[edit]
The main function of spermatocytes is to participate in spermatogenesis, the process of producing spermatozoa. This involves two rounds of meiosis, resulting in four haploid cells from each original spermatogonium.