Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Duloxetine.svg|Duloxetine | |||
File:Timeline-SNRIs-2010.png|Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor | |||
File:Desvenlafaxine.svg|Desvenlafaxine | |||
File:Duloxetine.svg|Duloxetine | |||
File:Levomilnacipran.svg|Levomilnacipran | |||
File:Milnacipran structure.svg|Milnacipran | |||
File:Sibutramine.svg|Sibutramine | |||
File:Tramadol.svg|Tramadol | |||
File:Venlafaxine structure.svg|Venlafaxine | |||
File:Timeline-history-2010.png|Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor | |||
File:SynapseSchematic en.svg|Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor | |||
File:Aryloxypropanamine scaffold.svg|Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:00, 20 February 2025
Serotonin–Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor
The Serotonin–Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor (SNRI) is a class of antidepressant drugs that treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs work by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain by inhibiting their reuptake into cells.
Etymology[edit]
The term "Serotonin–Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor" is derived from the drug's mechanism of action. It inhibits the reuptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine, thereby increasing their levels in the brain.
History[edit]
The first SNRI, venlafaxine, was introduced by Wyeth in 1993. The FDA approved it for the treatment of depression, and later for anxiety disorders and certain types of pain. Following venlafaxine, the next SNRI to be approved was duloxetine (Cymbalta) by Eli Lilly in 2004. Duloxetine was approved for the treatment of major depression and neuropathic pain.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
SNRIs work by inhibiting the reuptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine. This results in an increase in the extracellular concentrations of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in neurotransmission.
Related Terms[edit]
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitors (NDRIs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
See Also[edit]
|
|
|
-
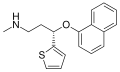
Duloxetine
-
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
-
Desvenlafaxine
-
Duloxetine
-
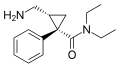
Levomilnacipran
-
Milnacipran
-
Sibutramine
-
Tramadol
-
Venlafaxine
-
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
-
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
-
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor