Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | |
| Complications | |
| Onset | Prior to age 12 |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic (inherited, de novo) and to a lesser extent, environmental factors (exposure to biohazards during pregnancy, traumatic brain injury) |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Based on impairing symptoms after other possible causes have been ruled out |
| Differential diagnosis |
|
| Prevention | |
| Treatment |
|
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | 0.8–1.5% (2019, using DSM-IV-TR and ICD-10) |
| Deaths | |
Overview of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)[edit]

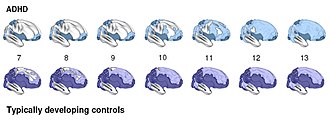

Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with daily functioning and developmental milestones. It is one of the most common mental health disorders diagnosed during childhood and often continues into adulthood.
ADHD affects multiple domains of life, including academic performance, workplace productivity, social interactions, and emotional well-being. It manifests as a persistent difficulty in maintaining attention, controlling impulses, and regulating activity levels. The disorder encompasses three primary presentations:
- Predominantly inattentive presentation
- Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation
- Combined presentation
History of ADHD[edit]
The recognition and study of ADHD have evolved significantly over the past century. The term "hyperkinetic impulse disorder" was used in early 20th-century literature to describe children displaying extreme restlessness. In 1980, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) introduced the term "Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD)," later expanded to ADHD in subsequent editions.
Diagnostic Criteria[edit]
ADHD is diagnosed using the criteria outlined in the DSM-5 (Fifth Edition), which requires the presence of symptoms for at least six months in multiple settings. Symptoms are classified under:
- Inattention: Difficulty sustaining focus, frequent mistakes in tasks, and forgetfulness in daily activities.
- Hyperactivity and Impulsivity: Fidgeting, inability to remain seated, excessive talking, and interrupting others.
For a diagnosis, symptoms must: 1. Be inappropriate for the individual's developmental level. 2. Cause significant impairment in social, academic, or occupational functioning. 3. Onset must occur before the age of 12.
Prevalence and Epidemiology[edit]
ADHD affects an estimated 5-7% of children globally, with higher diagnosis rates in certain countries, such as the United States. In adults, prevalence rates are around 2-5%. The disorder is more commonly diagnosed in males than females, though females are more likely to exhibit the inattentive subtype.
Etiology[edit]
ADHD has a multifactorial origin, with contributions from:
- Genetics: Twin and family studies indicate a strong heritable component.
- Environmental Factors: Prenatal exposure to alcohol, nicotine, or environmental toxins like lead.
- Neurobiological Factors: Differences in brain structure and function, including reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex and altered dopamine signaling.
Common Misconceptions[edit]
There are several misconceptions surrounding ADHD, including:
- ADHD is merely "bad behavior" or a result of poor parenting.
- ADHD only affects children and "goes away" in adulthood.
- All individuals with ADHD are hyperactive.
Such misconceptions can lead to stigma and underdiagnosis, especially among girls and adults.
Symptoms of ADHD[edit]
ADHD symptoms are grouped into two main categories: inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. These symptoms can manifest differently depending on the individual's age, gender, and ADHD presentation.
Inattention[edit]
Symptoms of inattention may include:
- Difficulty focusing on tasks or activities.
- Frequent careless mistakes in schoolwork, at work, or during other activities.
- Trouble listening to others, even when spoken to directly.
- Struggling to follow through on instructions or organizing tasks.
- Losing items frequently, such as keys, school supplies, or wallets.
- Being easily distracted by external stimuli or thoughts.
- Forgetting daily responsibilities, like appointments or chores.
Hyperactivity and Impulsivity[edit]
Hyperactivity and impulsivity symptoms may include:
- Constant fidgeting or tapping hands or feet.
- Inability to stay seated in situations where it is expected, such as classrooms or meetings.
- Feeling restless and moving around in inappropriate situations.
- Talking excessively or blurting out answers before questions are completed.
- Difficulty waiting in lines or taking turns.
- Interrupting conversations or intruding into other people’s activities.
Variations Across Lifespan[edit]
ADHD symptoms may evolve with age:
- In Children: Hyperactivity is more pronounced, with frequent running, climbing, or inability to play quietly.
- In Adolescents: Increased inattention and organizational challenges, leading to academic difficulties.
- In Adults: Predominantly inattentive symptoms, such as missing deadlines, chronic procrastination, or forgetfulness.
Gender Differences[edit]
While ADHD is more commonly diagnosed in males, females often present with subtler symptoms, such as daydreaming and inattention, leading to underdiagnosis. Boys are more likely to display externalized behaviors like hyperactivity, whereas girls may struggle silently with focus and emotional regulation.
Diagnostic Process[edit]
ADHD diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
- Clinical Interview: A detailed history of the individual’s symptoms, behavior, and developmental milestones.
- Behavioral Assessment: Reports from caregivers, teachers, or colleagues to understand symptom manifestation in multiple settings.
- Standardized Rating Scales: Tools such as the Conners' Rating Scales or the ADHD Rating Scale-IV help quantify symptoms.
- Rule Out Other Conditions: Differential diagnosis is critical to exclude conditions with overlapping symptoms, such as anxiety disorders, learning disabilities, or bipolar disorder.
Challenges in Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing ADHD is complex due to:
- Overlapping symptoms with other mental health conditions.
- Subjective assessments relying on self-reports or caregiver observations.
- Cultural biases affecting symptom interpretation.
- Underdiagnosis in girls and minority groups due to atypical symptom presentations.
Importance of Early Diagnosis[edit]
Early identification and intervention are essential to:
- Prevent academic and social difficulties.
- Support self-esteem and emotional regulation.
- Reduce the risk of secondary issues, such as anxiety, depression, or substance use disorders.
Treatment Overview[edit]
The management of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) often requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s symptoms, age, and needs. Treatment options include behavioral therapy, medication, educational support, and lifestyle adjustments. Early and consistent interventions can significantly improve outcomes.
Behavioral Therapy[edit]
Behavioral therapy is a cornerstone of ADHD treatment, particularly for children and adolescents.
Parent Training[edit]
Parent training in behavior management (PTBM) equips caregivers with strategies to:
- Reinforce positive behaviors through praise and rewards.
- Implement consistent disciplinary actions for undesirable behaviors.
- Improve parent-child communication and reduce stress at home.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)[edit]
CBT is effective in addressing ADHD-related challenges, such as:
- Time management and organizational skills.
- Emotional regulation and impulse control.
- Managing coexisting conditions like anxiety and depression.
School-Based Interventions[edit]
Collaboration with educators and school staff can help:
- Develop Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) or 504 Plans.
- Implement classroom accommodations, such as:
- Preferential seating.
- Extended test times.
- Structured routines.
- Use behavioral charts to reinforce task completion and participation.
Social Skills Training[edit]
Children with ADHD often benefit from structured training to:
- Improve peer interactions.
- Recognize social cues.
- Resolve conflicts effectively.
Pharmacological Treatment[edit]
Medication is a primary treatment option for moderate to severe ADHD symptoms, particularly when behavioral therapy alone is insufficient.
Stimulant Medications[edit]
Stimulants are the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD. They increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, enhancing focus and impulse control. Common stimulants include:
- Methylphenidate: (e.g., Ritalin, Concerta)
- Amphetamine derivatives: (e.g., Adderall, Vyvanse)
Benefits[edit]
- Rapid symptom improvement.
- High efficacy in managing inattention and hyperactivity.
Side Effects[edit]
- Decreased appetite.
- Insomnia.
- Irritability or mood swings.
- Increased heart rate or blood pressure.
Non-Stimulant Medications[edit]
Non-stimulant options are useful for individuals who experience side effects from stimulants or have coexisting conditions. These include:
- Atomoxetine (Strattera): Increases norepinephrine activity.
- Guanfacine (Intuniv): Targets impulse control and emotional dysregulation.
- Clonidine: Often used to address sleep disturbances.
Lifestyle Modifications[edit]
Lifestyle changes can complement medical and behavioral interventions.
Diet and Nutrition[edit]
While no specific diet treats ADHD, balanced nutrition can support overall brain function:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish and flaxseed, these may enhance cognitive function.
- Avoidance of artificial additives: Some children benefit from limiting preservatives and food coloring.
Physical Activity[edit]
Regular exercise:
- Improves focus and emotional regulation.
- Reduces hyperactivity and impulsivity.
- Enhances overall mental well-being.
Sleep Hygiene[edit]
Many individuals with ADHD struggle with sleep disorders. Strategies to improve sleep include:
- Maintaining a consistent bedtime routine.
- Avoiding screen time before bed.
- Using white noise machines or weighted blankets for relaxation.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies[edit]
Alternative treatments may offer additional support but should be used alongside evidence-based approaches.
Mindfulness and Meditation[edit]
Practices like mindfulness meditation can help:
Neurofeedback[edit]
This technique uses real-time monitoring of brain activity to train individuals to improve focus and reduce ADHD symptoms. While promising, more research is needed to confirm its long-term effectiveness.
Herbal Supplements[edit]
Some parents explore herbal remedies like ginkgo biloba or ginseng for cognitive support. However, these should be used cautiously and under medical supervision.
Combined Treatment Approaches[edit]
Most individuals with ADHD benefit from a combination of therapies, such as behavioral interventions paired with medication. Collaborative care involving parents, educators, and healthcare providers ensures the most comprehensive and effective management plan.
The Impact of ADHD on Daily Life[edit]
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects various aspects of life, influencing academic performance, workplace productivity, relationships, and mental health. Understanding these impacts can guide individuals and caregivers in managing the condition effectively.
Academic Challenges[edit]
Children and adolescents with ADHD often face difficulties in school due to:
- Inattention leading to missed instructions or incomplete assignments.
- Hyperactivity causing classroom disruptions.
- Impulsivity resulting in poor decision-making.
These challenges can lead to lower grades, school avoidance, and disciplinary issues. However, with proper interventions such as Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) and classroom accommodations, many students with ADHD can thrive academically.
Workplace Implications[edit]
Adults with ADHD may experience:
- Difficulty with time management and meeting deadlines.
- Challenges maintaining focus during meetings or tasks.
- Impulsive behaviors that affect workplace relationships.
Employers can support employees with ADHD by offering:
- Flexible schedules.
- Breaks for physical activity to reduce hyperactivity.
- Clear and structured expectations.
Relationship Struggles[edit]
ADHD can strain personal relationships, including those with:
- Family members, who may feel overwhelmed by the individual’s behaviors.
- Romantic partners, due to communication breakdowns or impulsive actions.
- Peers, as social cues may be misunderstood.
Therapies like family counseling and social skills training can help improve interpersonal relationships.
Emotional and Mental Health[edit]
Individuals with ADHD are at a higher risk for comorbid conditions, such as:
- Anxiety disorders.
- Depression.
- Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) or conduct disorder (CD) in children.
Proactive mental health care, including therapy and medication, can mitigate these risks and enhance overall well-being.
Coping Strategies for Individuals with ADHD[edit]
Adopting effective coping strategies can empower individuals with ADHD to navigate challenges successfully.
Organizational Skills[edit]
Improving organizational skills can reduce procrastination and task overload:
- Use planners or digital apps to manage schedules.
- Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Set timers for focused work sessions.
Time Management[edit]
Time management strategies include:
- Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance.
- Using visual aids, such as calendars and checklists.
- Allocating specific time blocks for activities and adhering to them.
Mindfulness Techniques[edit]
Practicing mindfulness can help individuals manage stress and improve focus:
- Engage in deep breathing exercises.
- Participate in yoga or meditation.
- Practice grounding techniques during moments of overwhelm.
Building a Support Network[edit]
A strong support system can make a significant difference:
- Join ADHD support groups to share experiences and learn strategies.
- Seek guidance from teachers, mentors, and healthcare professionals.
- Involve family members in treatment plans to foster understanding.
Utilizing Technology[edit]
Technology can assist individuals with ADHD in staying organized and productive:
- Use reminder apps for appointments and deadlines.
- Explore noise-canceling headphones to minimize distractions.
- Leverage task management tools, like Trello or Asana, for work and school projects.
Parenting a Child with ADHD[edit]
Parents of children with ADHD play a critical role in their development and success.
Positive Reinforcement[edit]
- Praise and reward desirable behaviors consistently.
- Create a system of incentives for completing tasks or following rules.
Setting Routines[edit]
- Establish predictable daily routines for activities like meals, homework, and bedtime.
- Use visual schedules or charts to help children understand expectations.
Encouraging Physical Activity[edit]
- Promote regular exercise to manage hyperactivity and improve focus.
- Engage children in team sports or outdoor play.
Partnering with Schools[edit]
- Communicate frequently with teachers to monitor progress and address concerns.
- Advocate for accommodations that suit the child’s unique needs.
Long-Term Outlook[edit]
With the right support and strategies, individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling lives. Success stories abound of people who, with effective management, excel in their fields and build meaningful relationships. Early diagnosis, consistent intervention, and a supportive environment are key to unlocking their potential.
Glossary of ADHD-Related Terms[edit]
A[edit]
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): A neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Attention: The ability to focus on a specific task, thought, or activity.
Attention deficit disorder (ADD): An outdated term previously used to describe ADHD without hyperactivity.
B[edit]
Behavioral therapy: A form of psychotherapy that focuses on changing negative behaviors, often used in ADHD treatment.
Brain imaging studies: Techniques like MRI and fMRI used to observe brain activity and structure in individuals with ADHD.
C[edit]
Central nervous system (CNS): The part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, where ADHD-related dysfunctions are often observed.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): A structured, goal-oriented form of therapy that can help individuals with ADHD develop coping strategies.
Comorbidity: The presence of one or more additional disorders or diseases occurring with ADHD, such as anxiety disorders or depression.
Concentration: The ability to sustain attention on a task, often impaired in individuals with ADHD.
D[edit]
Dopamine: A neurotransmitter involved in reward, motivation, and attention; often implicated in ADHD.
Diagnosis: The process of identifying ADHD through medical evaluation, observation, and standardized criteria, such as those outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM).
E[edit]
Executive function: A set of mental skills including working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control, often impaired in individuals with ADHD.
Environmental factors: External influences such as diet, parenting, and schooling that may impact ADHD symptoms.
H[edit]
Hyperactivity: Excessive movement, restlessness, and difficulty sitting still, a key symptom of ADHD.
Hypoactivity: Reduced levels of activity and energy, less commonly associated with ADHD but observed in some individuals.
I[edit]
Inattention: Difficulty sustaining focus, listening, or completing tasks, one of the core symptoms of ADHD.
Impulsivity: Acting without thinking or considering the consequences, another core symptom of ADHD.
Intervention: Strategies and treatments, such as behavioral therapy or medication, aimed at managing ADHD symptoms.
M[edit]
Medication: Pharmaceutical treatments like stimulants (e.g., methylphenidate, amphetamine) and non-stimulants (e.g., atomoxetine) used to manage ADHD symptoms.
Multimodal treatment: Combining various approaches, such as medication, behavioral therapy, and educational support, to treat ADHD.
N[edit]
Neurodevelopmental disorder: A category of disorders that affect brain development, including ADHD.
Neurotransmitters: Chemicals like dopamine and norepinephrine that transmit signals in the brain and play a role in ADHD.
O[edit]
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD): A common comorbid condition with ADHD, characterized by defiant and disobedient behavior.
P[edit]
Parent training: Educational programs that teach parents strategies to manage their child’s ADHD symptoms effectively.
Prefrontal cortex: The region of the brain associated with executive functions, often underactive in individuals with ADHD.
S[edit]
Self-regulation: The ability to manage emotions, behavior, and impulses, typically impaired in ADHD.
Stimulants: A class of drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system, commonly prescribed for ADHD.
T[edit]
Time management: The ability to plan and control how one spends time, often challenging for individuals with ADHD.
Treatment-resistant ADHD: Cases where symptoms persist despite multiple interventions, requiring specialized strategies.
W[edit]
Working memory: The ability to hold and manipulate information temporarily, often impaired in individuals with ADHD.
See also[edit]
- Glossary of ADHD terms
- Adult attention-deficit disorder
- ADHD psychosis
- Anti-psychiatry
- Auditory processing disorder
- Chemical imbalance theory
- Controversy about ADHD
- Developmental disability
- Educational psychology
- Hyperactivity
- Hyperfocus
- List of fictional characters with ADHD
- List of famous people with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
- National Institute of Mental Health
- Sensory integration disorder
- Sluggish cognitive tempo
- Texas Medication Algorithm Project
- David Keirsey
External links[edit]
- NIMH's ADHD page
- National Resource Center on AD/HD
- Article: Omega-3 Oils and Your Child's Behavior and Learning
- NIH - Diagnosis and Treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- CDC's ADHD page
- ADD Forums
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids Benefits and ADHD
|
|
|
| Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Category
|
| ADHD pharmacotherapies | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Emotional and behavioral disorders | ||
|---|---|---|
|
| Digital media use and mental health | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


