Clotiapine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Clotiapine == | |||
<gallery> | |||
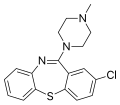
File:Clotiapine.svg|Chemical structure of Clotiapine | |||
File:Clotiapine_ball-and-stick_model.png|Ball-and-stick model of Clotiapine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 02:09, 17 February 2025
Clotiapine is an atypical antipsychotic medication. It is primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Clotiapine was first synthesized in the 1960s and is marketed under various brand names across the world.
Etymology[edit]
The name "Clotiapine" is derived from the chemical structure of the drug, which is a derivative of the dibenzothiazepine class of compounds. The "clotia-" prefix is a contraction of "chlorothiazepine", referring to the presence of a chlorine atom and a thiazepine ring in the molecule.
Pharmacology[edit]
Clotiapine acts as an antagonist at various receptor sites in the brain. It has high affinity for the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, and the dopamine D1, D2, D3, and D4 receptors. It also has affinity for the histamine H1 and adrenergic α1 receptors. The antipsychotic effects of clotiapine are thought to be primarily due to its antagonism of the D2 receptors in the mesolimbic pathway, which is implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Clinical Use[edit]
Clotiapine is used in the treatment of acute and chronic schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. It is also used off-label for the treatment of insomnia and anxiety disorders. The drug has a rapid onset of action, with antipsychotic effects observed within the first week of treatment.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of clotiapine include sedation, orthostatic hypotension, dry mouth, constipation, and weight gain. Less common side effects include extrapyramidal symptoms, tardive dyskinesia, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.