A-234 (nerve agent): Difference between revisions
CSV import Tag: Reverted |
Tag: Manual revert |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[[Category:Organophosphates]] | [[Category:Organophosphates]] | ||
[[Category:Chemical warfare agents]] | [[Category:Chemical warfare agents]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:51, 17 February 2025
A-234 (nerve agent)
Chemical compound
A-234 is a nerve agent of the Novichok agent family, developed in the Soviet Union and Russia from the 1970s to the 1990s. It is one of the most potent nerve agents known, with a mechanism of action similar to other organophosphate nerve agents such as sarin and VX.
Chemical structure and properties[edit]
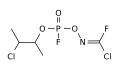
A-234 is an organophosphate compound, characterized by the presence of a phosphorus atom bonded to an oxygen atom and a fluorine atom, as well as a carbon-containing group. The chemical structure of A-234 is similar to other Novichok agents, which are designed to be more toxic and harder to detect than earlier nerve agents.


Mechanism of action[edit]
A-234, like other nerve agents, inhibits the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which is responsible for breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. This inhibition leads to an accumulation of acetylcholine, resulting in continuous stimulation of muscles, glands, and central nervous system structures. The overstimulation causes symptoms such as muscle twitching, paralysis, respiratory failure, and potentially death.
Symptoms of exposure[edit]
Exposure to A-234 can cause a range of symptoms, depending on the dose and route of exposure. Symptoms may include:
- Miosis (constricted pupils)
- Bronchorrhea (excessive secretion of mucus in the airways)
- Bronchospasm (constriction of the airways)
- Muscle fasciculations (involuntary muscle contractions)
- Seizures
- Coma
- Respiratory failure
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for A-234 poisoning is similar to that for other nerve agents and includes the administration of atropine, an anticholinergic drug that blocks the effects of acetylcholine, and pralidoxime, which reactivates acetylcholinesterase. Benzodiazepines may also be used to control seizures.
History and development[edit]
The development of A-234 and other Novichok agents was part of a secret Soviet program aimed at creating more effective chemical weapons that could evade international detection and control measures. The existence of these agents was revealed by Vil Mirzayanov, a former Soviet scientist, in the 1990s.
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Chemical structure of A-234 as described by Mirzayanov
-
Alternative chemical structure of A-234 as described by Hoenig