Acetyl-CoA: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[[Category:Biochemistry]] | [[Category:Biochemistry]] | ||
[[Category:Metabolism]] | [[Category:Metabolism]] | ||
== Acetyl-CoA == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Acetyl-CoA-2D_colored.svg|2D structure of Acetyl-CoA | |||
File:Acetyl-CoA-3D-balls.png|3D ball-and-stick model of Acetyl-CoA | |||
File:Acetyl-CoA-3D-vdW.png|3D van der Waals model of Acetyl-CoA | |||
File:Pyruvate_dehydrogenase_complex_reaction.svg|Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reaction | |||
File:Metabolism4.jpg|Metabolism overview | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:56, 18 February 2025
Acetyl-CoA[edit]

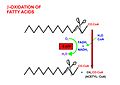
Acetyl-CoA is a central metabolite in biochemistry, playing a critical role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It is a key molecule in the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) and is involved in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids.
Structure[edit]
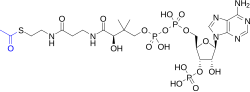
Acetyl-CoA is a complex molecule composed of an acetyl group attached to coenzyme A. The acetyl group is derived from pyruvate, which is the end product of glycolysis. Coenzyme A is a large molecule that contains a pantothenic acid moiety, a cysteamine group, and a 3'-phosphoadenosine diphosphate.
Function[edit]
Acetyl-CoA serves as a substrate for several important biochemical pathways:
- Citric Acid Cycle: Acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle by combining with oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Fatty Acid Synthesis: Acetyl-CoA is a precursor for the synthesis of fatty acids. It is converted to malonyl-CoA by the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which is the first step in fatty acid biosynthesis.
- Ketone Body Production: In the liver, acetyl-CoA can be converted into ketone bodies during periods of low carbohydrate intake or prolonged exercise.
- Cholesterol Synthesis: Acetyl-CoA is also a precursor for the synthesis of cholesterol and other isoprenoids.
Metabolic Pathways[edit]
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex[edit]

The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is a multi-enzyme complex that converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA. This reaction links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle and is a key regulatory point in cellular metabolism.
Beta-Oxidation[edit]
In the process of beta-oxidation, fatty acids are broken down into acetyl-CoA units, which can then enter the citric acid cycle for energy production.
Amino Acid Catabolism[edit]
Certain amino acids can be converted into acetyl-CoA through various catabolic pathways, contributing to the pool of acetyl-CoA available for energy production and biosynthesis.
Importance in Metabolism[edit]

Acetyl-CoA is a pivotal molecule in metabolism, acting as a crossroads for various metabolic pathways. Its central role in energy production and biosynthesis makes it essential for cellular function and survival.
Related Pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
3D van der Waals model of Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA[edit]
-
2D structure of Acetyl-CoA
-
3D ball-and-stick model of Acetyl-CoA
-
3D van der Waals model of Acetyl-CoA
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reaction
-
Metabolism overview