Human Development Index: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
* [[United Nations Development Programme]] | * [[United Nations Development Programme]] | ||
{{Human | {{Human development}} | ||
[[Category:Development economics]] | [[Category:Development economics]] | ||
[[Category:United Nations]] | [[Category:United Nations]] | ||
[[Category:International rankings]] | [[Category:International rankings]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:41, 6 January 2025
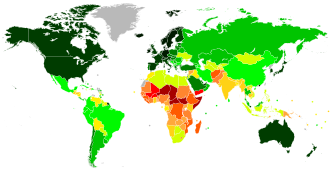



The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which are used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. It was introduced by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in 1990 as a measure of a country's social and economic development.
Components of the HDI[edit]
The HDI is calculated using three key dimensions:
1. Life Expectancy[edit]
This dimension measures the average number of years a newborn is expected to live if current mortality rates continue to apply. It reflects the ability of a country to provide a healthy and long life for its citizens.
2. Education[edit]
The education dimension is assessed by two indicators:
- Mean years of schooling: The average number of years of education received by people ages 25 and older, adjusted for the highest level of education attained.
- Expected years of schooling: The total number of years of schooling that a child of school entrance age can expect to receive if prevailing patterns of age-specific enrollment rates persist throughout the child's life.
3. Income[edit]
The income dimension is measured by Gross National Income (GNI) per capita. It reflects the standard of living and is adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP) to account for differences in cost of living and inflation rates between countries.
Calculation of the HDI[edit]
The HDI is calculated as the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of the three dimensions. The formula is:
HDI = \( \sqrt[3]{\text{Life Expectancy Index} \times \text{Education Index} \times \text{Income Index}} \)
Each dimension index is calculated as follows:
\[ \text{Dimension Index} = \frac{\text{Actual Value} - \text{Minimum Value}}{\text{Maximum Value} - \text{Minimum Value}} \]
The maximum and minimum values are set by the UNDP to allow for comparability across countries.
Criticisms and Limitations[edit]
While the HDI is a widely used measure of development, it has several limitations:
- It does not account for inequalities, poverty, human security, and empowerment.
- It does not consider environmental sustainability.
- The HDI is a summary measure and may not capture the full complexity of human development.
Recent Developments[edit]
The UNDP has introduced additional indices to address some of the HDI's limitations, such as the Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI), the Gender Development Index (GDI), and the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
Also see[edit]
- Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index
- Gender Development Index
- Multidimensional Poverty Index
- Gross National Income
- United Nations Development Programme
| Development of the human body | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|