Trisodium citrate: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Trisodium citrate}} | ||
== | == Trisodium citrate == | ||
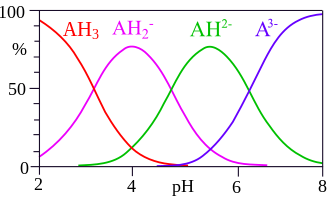
[[File:Citric_acid_speciation.svg|thumb|right|Speciation of citric acid in solution]] | |||
Trisodium citrate, also known as sodium citrate, is the sodium salt of [[citric acid]]. It possesses the chemical formula Na_C_H_O_ and is commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Trisodium citrate is a white, crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water and has a slightly salty, tart flavor. | |||
== | == Chemical Properties == | ||
Trisodium citrate is derived from citric acid, a weak organic acid that is naturally found in citrus fruits. The compound is formed by neutralizing citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. In aqueous solution, trisodium citrate dissociates into three sodium ions and one citrate ion. | |||
=== Speciation === | |||
The speciation of citric acid in solution is an important aspect of understanding the behavior of trisodium citrate. As shown in the diagram, citric acid can exist in multiple forms depending on the pH of the solution. At higher pH levels, the citrate ion predominates, which is the form present in trisodium citrate solutions. | |||
== | == Uses == | ||
Trisodium citrate is widely used in the food industry as an [[emulsifier]], [[preservative]], and [[flavoring agent]]. It is commonly found in beverages, dairy products, and processed foods. In the pharmaceutical industry, trisodium citrate is used as an [[anticoagulant]] in blood collection tubes and as a buffering agent in medications. | |||
== | === Food Industry === | ||
In the food industry, trisodium citrate acts as a [[pH buffer]] and helps maintain the stability of emulsions. It is often used in [[carbonated beverages]] to enhance flavor and in [[cheese]] production to improve texture. | |||
[[Category: | === Medical Applications === | ||
[[Category: | In medicine, trisodium citrate is used to prevent blood clotting during [[blood transfusions]] and in [[dialysis]] treatments. It is also used in [[oral rehydration solutions]] to treat dehydration. | ||
== Safety == | |||
Trisodium citrate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. However, excessive consumption may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort. | |||
== Related pages == | |||
* [[Citric acid]] | |||
* [[Sodium bicarbonate]] | |||
* [[Emulsifier]] | |||
* [[Anticoagulant]] | |||
[[Category:Food additives]] | |||
[[Category:Pharmaceuticals]] | |||
[[Category:Sodium compounds]] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:27, 16 February 2025
Trisodium citrate[edit]
Trisodium citrate, also known as sodium citrate, is the sodium salt of citric acid. It possesses the chemical formula Na_C_H_O_ and is commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Trisodium citrate is a white, crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water and has a slightly salty, tart flavor.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Trisodium citrate is derived from citric acid, a weak organic acid that is naturally found in citrus fruits. The compound is formed by neutralizing citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. In aqueous solution, trisodium citrate dissociates into three sodium ions and one citrate ion.
Speciation[edit]
The speciation of citric acid in solution is an important aspect of understanding the behavior of trisodium citrate. As shown in the diagram, citric acid can exist in multiple forms depending on the pH of the solution. At higher pH levels, the citrate ion predominates, which is the form present in trisodium citrate solutions.
Uses[edit]
Trisodium citrate is widely used in the food industry as an emulsifier, preservative, and flavoring agent. It is commonly found in beverages, dairy products, and processed foods. In the pharmaceutical industry, trisodium citrate is used as an anticoagulant in blood collection tubes and as a buffering agent in medications.
Food Industry[edit]
In the food industry, trisodium citrate acts as a pH buffer and helps maintain the stability of emulsions. It is often used in carbonated beverages to enhance flavor and in cheese production to improve texture.
Medical Applications[edit]
In medicine, trisodium citrate is used to prevent blood clotting during blood transfusions and in dialysis treatments. It is also used in oral rehydration solutions to treat dehydration.
Safety[edit]
Trisodium citrate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. However, excessive consumption may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort.