Droloxifene: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Droloxifene''' is a [[ | {{Short description|Overview of the drug Droloxifene}} | ||
{{Drugbox | |||
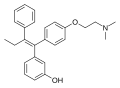
| image = Droloxifene.svg | |||
| image_size = 250px | |||
| image_alt = Structural formula of Droloxifene | |||
}} | |||
'''Droloxifene''' is a [[selective estrogen receptor modulator]] (SERM) that has been studied for its potential use in the treatment of [[breast cancer]] and [[osteoporosis]]. It is a nonsteroidal compound that exhibits both estrogenic and antiestrogenic properties depending on the target tissue. | |||
==Pharmacology== | |||
Droloxifene acts by binding to [[estrogen receptors]] in various tissues. In breast tissue, it functions as an antiestrogen, blocking the proliferative actions of estrogen and thereby inhibiting the growth of estrogen-dependent tumors. Conversely, in bone tissue, droloxifene acts as an estrogen agonist, helping to maintain bone density and reduce the risk of fractures. | |||
==Mechanism of Action== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Droloxifene | Droloxifene's mechanism of action involves its interaction with estrogen receptors, which are nuclear hormone receptors. Upon binding to these receptors, droloxifene can modulate the transcription of estrogen-responsive genes. This dual action is what classifies it as a selective estrogen receptor modulator. | ||
==Clinical Applications== | ==Clinical Applications== | ||
Droloxifene has been primarily investigated for its role in the management of breast cancer. Its ability to act as an antiestrogen in breast tissue makes it a candidate for reducing the risk of cancer recurrence in patients with estrogen receptor-positive tumors. Additionally, its bone-preserving effects have been explored for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. | |||
== | ==Side Effects== | ||
As with | As with other SERMs, droloxifene may cause side effects such as hot flashes, leg cramps, and an increased risk of thromboembolic events. The risk-benefit profile of droloxifene must be carefully considered in clinical settings. | ||
== | ==Research and Development== | ||
Droloxifene has undergone various phases of clinical trials to evaluate its efficacy and safety. While promising results have been observed, further studies are needed to fully establish its therapeutic potential and to compare its effectiveness with other SERMs like [[tamoxifen]] and [[raloxifene]]. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Selective | * [[Selective estrogen receptor modulator]] | ||
* [[Breast | * [[Breast cancer treatment]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Osteoporosis]] | ||
[[Category:Selective | [[Category:Selective estrogen receptor modulators]] | ||
[[Category:Breast | [[Category:Breast cancer]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Osteoporosis]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Droloxifene.svg|Droloxifene | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:02, 20 February 2025
Overview of the drug Droloxifene
| Droloxifene | |
|---|---|

| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Droloxifene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that has been studied for its potential use in the treatment of breast cancer and osteoporosis. It is a nonsteroidal compound that exhibits both estrogenic and antiestrogenic properties depending on the target tissue.
Pharmacology[edit]
Droloxifene acts by binding to estrogen receptors in various tissues. In breast tissue, it functions as an antiestrogen, blocking the proliferative actions of estrogen and thereby inhibiting the growth of estrogen-dependent tumors. Conversely, in bone tissue, droloxifene acts as an estrogen agonist, helping to maintain bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Droloxifene's mechanism of action involves its interaction with estrogen receptors, which are nuclear hormone receptors. Upon binding to these receptors, droloxifene can modulate the transcription of estrogen-responsive genes. This dual action is what classifies it as a selective estrogen receptor modulator.
Clinical Applications[edit]
Droloxifene has been primarily investigated for its role in the management of breast cancer. Its ability to act as an antiestrogen in breast tissue makes it a candidate for reducing the risk of cancer recurrence in patients with estrogen receptor-positive tumors. Additionally, its bone-preserving effects have been explored for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
Side Effects[edit]
As with other SERMs, droloxifene may cause side effects such as hot flashes, leg cramps, and an increased risk of thromboembolic events. The risk-benefit profile of droloxifene must be carefully considered in clinical settings.
Research and Development[edit]
Droloxifene has undergone various phases of clinical trials to evaluate its efficacy and safety. While promising results have been observed, further studies are needed to fully establish its therapeutic potential and to compare its effectiveness with other SERMs like tamoxifen and raloxifene.
Related pages[edit]
-
Droloxifene