Methyldiazinol: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[Category:Organic compounds]] | [[Category:Organic compounds]] | ||
{{Chem-stub}} | {{Chem-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
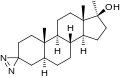
File:Methyldiazirinol.svg|Methyldiazinol | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:36, 20 February 2025
Methyldiazinol is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C3H6N2O. It is a member of the diazines, which are six-membered cyclic compounds containing two nitrogen atoms. Methyldiazinol is a liquid at room temperature and is used in various chemical syntheses.
Structure and Properties[edit]
Methyldiazinol consists of a six-membered ring with two nitrogen atoms and four carbon atoms. One of the carbon atoms is substituted with a methyl group, hence the name "methyldiazinol". The molecule is planar due to the sp2 hybridization of the carbon and nitrogen atoms in the ring.
The compound has a molar mass of 86.09 g/mol. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature and has a boiling point of 101-102 °C. Methyldiazinol is soluble in water and most organic solvents.
Synthesis[edit]
Methyldiazinol can be synthesized by the reaction of diazomethane with formaldehyde in the presence of a base. The reaction proceeds via a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, which is a type of pericyclic reaction.
Applications[edit]
Methyldiazinol is used as a building block in the synthesis of various organic compounds. It can be used to prepare pyridines, pyrimidines, and other nitrogen-containing heterocycles. It is also used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Safety[edit]
Like many diazines, methyldiazinol is potentially hazardous. It can cause skin and eye irritation, and prolonged exposure can lead to respiratory problems. It is recommended to handle this compound in a well-ventilated area and to use appropriate personal protective equipment.
See Also[edit]
-
Methyldiazinol