Central Europe: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{Europe-stub}} | {{Europe-stub}} | ||
{{food-stub}} | {{food-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Central Europe (Brockhaus).svg|Central Europe (Brockhaus) | |||
File:Grossgliederung Europas-en.svg|Grossgliederung Europas | |||
File:Central Europe 1902.PNG|Central Europe 1902 | |||
File:Central Europe (Geographie universelle, 1927).svg|Central Europe (Geographie universelle, 1927) | |||
File:Avantgarde CE.svg|Avantgarde Central Europe | |||
File:World War II in Europe, 1942.svg|World War II in Europe, 1942 | |||
File:Neutral and Non-Aligned European States.png|Neutral and Non-Aligned European States | |||
File:Floristic regions in Europe (english).png|Floristic regions in Europe | |||
File:Carpathian Basin-Pannonian Basin.jpg|Carpathian Basin-Pannonian Basin | |||
File:Mapcarpat2.png|Map of the Carpathians | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 05:51, 3 March 2025
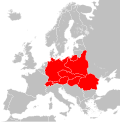
Central Europe is a region located in the heart of the European continent. It is primarily composed of various countries including Germany, Austria, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Poland, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. The region is known for its rich history, diverse culture, and significant contributions to global affairs.
Geography[edit]
Central Europe is characterized by its landlocked geography, with the Alps and Carpathian Mountains serving as natural boundaries. The region is also home to several major rivers including the Danube, Elbe, and Vistula.
History[edit]
The history of Central Europe is marked by a series of significant events, from the rise and fall of the Holy Roman Empire to the impacts of the two World Wars. The region has also been shaped by the influences of various empires and cultures, including the Roman Empire, Ottoman Empire, and Habsburg Monarchy.
Culture[edit]
Central Europe boasts a rich and diverse culture, with influences from both Western and Eastern Europe. The region is known for its contributions to literature, music, art, and philosophy, with notable figures such as Franz Kafka, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Sigmund Freud hailing from this region.
Economy[edit]
The economy of Central Europe is diverse and robust, with strong sectors in manufacturing, services, and agriculture. Several Central European countries are members of the European Union and the Eurozone, contributing significantly to the overall European economy.
Politics[edit]
The political landscape of Central Europe is diverse, with a mix of parliamentary and presidential systems. Many Central European countries are members of international organizations such as the United Nations, NATO, and the European Union.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
Central Europe (Brockhaus)
-
Grossgliederung Europas
-
Central Europe 1902
-
Central Europe (Geographie universelle, 1927)
-
Avantgarde Central Europe
-
World War II in Europe, 1942
-
Neutral and Non-Aligned European States
-
Floristic regions in Europe
-
Carpathian Basin-Pannonian Basin
-
Map of the Carpathians