Ceftolozane/tazobactam: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
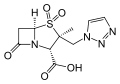
File:Ceftolozane.svg|Ceftolozane | |||
File:Tazobactam.svg|Tazobactam | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:49, 17 February 2025
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is a combination antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is a combination of ceftolozane, a cephalosporin antibiotic, and tazobactam, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. This combination is used to treat certain types of infections caused by bacteria such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and infections of the abdomen.
Medical uses[edit]
Ceftolozane/tazobactam is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It is a combination of two drugs: ceftolozane, which is a cephalosporin antibiotic that works by stopping the growth of bacteria, and tazobactam, which is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that helps to prevent resistance to the antibiotic.
Side effects[edit]
Common side effects of ceftolozane/tazobactam include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Serious side effects may include allergic reactions, Clostridium difficile infection, and seizures.
Mechanism of action[edit]
Ceftolozane works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to cell death. Tazobactam works by inhibiting beta-lactamase enzymes, preventing them from breaking down ceftolozane and thus increasing its effectiveness.
History[edit]
Ceftolozane/tazobactam was approved for medical use in the United States in 2014. It is marketed under the brand name Zerbaxa by Merck & Co.