Dibekacin: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An aminoglycoside antibiotic}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477002123 | |||
| image = Dibekacin.svg | |||
| image2 = | |||
}} | |||
'''Dibekacin''' is an [[aminoglycoside]] [[antibiotic]] used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. It is particularly effective against [[Gram-negative bacteria]] and is often used in clinical settings where other antibiotics may not be effective. | |||
Dibekacin | |||
== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Dibekacin | Dibekacin works by binding to the 30S subunit of the bacterial [[ribosome]], inhibiting protein synthesis. This action is bactericidal, meaning it kills bacteria rather than merely inhibiting their growth. The binding interferes with the initiation complex of peptide formation, causing misreading of mRNA, which leads to the production of nonfunctional or toxic peptides. | ||
== | ==Clinical Uses== | ||
Dibekacin is primarily used to treat serious infections caused by susceptible strains of bacteria. These include: | |||
* [[Sepsis]] | |||
* [[Pneumonia]] | |||
* [[Urinary tract infections]] | |||
* [[Intra-abdominal infections]] | |||
It is often reserved for use in hospital settings due to its potential for nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, which are common side effects of aminoglycosides. | |||
== | ==Administration== | ||
Dibekacin is usually administered via [[intravenous]] or [[intramuscular]] injection. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection, the patient's renal function, and the susceptibility of the causative organism. | |||
==Side Effects== | |||
Common side effects of dibekacin include: | |||
* [[Nephrotoxicity]] | |||
* [[Ototoxicity]] | |||
* [[Neuromuscular blockade]] | |||
Patients receiving dibekacin should be monitored for signs of renal impairment and auditory damage. Dosage adjustments may be necessary in patients with pre-existing renal conditions. | |||
==Resistance== | |||
Bacterial resistance to dibekacin can occur through several mechanisms, including: | |||
* Enzymatic modification of the drug | |||
* Alteration of the ribosomal binding site | |||
* Efflux pumps that remove the drug from the bacterial cell | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Aminoglycoside]] | * [[Aminoglycoside]] | ||
* [[Antibiotic]] | * [[Antibiotic resistance]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Gram-negative bacteria]] | ||
[[Category:Aminoglycoside antibiotics]] | |||
[[Category:Antibiotics]] | [[Category:Antibiotics]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Dibekacin.svg|Dibekacin | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:59, 20 February 2025
An aminoglycoside antibiotic
| Dibekacin | |
|---|---|
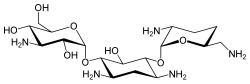
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Dibekacin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used in the treatment of various bacterial infections. It is particularly effective against Gram-negative bacteria and is often used in clinical settings where other antibiotics may not be effective.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Dibekacin works by binding to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting protein synthesis. This action is bactericidal, meaning it kills bacteria rather than merely inhibiting their growth. The binding interferes with the initiation complex of peptide formation, causing misreading of mRNA, which leads to the production of nonfunctional or toxic peptides.
Clinical Uses[edit]
Dibekacin is primarily used to treat serious infections caused by susceptible strains of bacteria. These include:
It is often reserved for use in hospital settings due to its potential for nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, which are common side effects of aminoglycosides.
Administration[edit]
Dibekacin is usually administered via intravenous or intramuscular injection. The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection, the patient's renal function, and the susceptibility of the causative organism.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of dibekacin include:
Patients receiving dibekacin should be monitored for signs of renal impairment and auditory damage. Dosage adjustments may be necessary in patients with pre-existing renal conditions.
Resistance[edit]
Bacterial resistance to dibekacin can occur through several mechanisms, including:
- Enzymatic modification of the drug
- Alteration of the ribosomal binding site
- Efflux pumps that remove the drug from the bacterial cell
Related pages[edit]
-
Dibekacin