Oncocytoma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Oncocytoma | |||
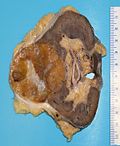
| image = [[File:Oncocytoma_of_the_Salivary_Gland.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = Oncocytoma of the salivary gland | |||
| field = [[Oncology]] | |||
| synonyms = Oncocytic adenoma | |||
| symptoms = Often asymptomatic, may present as a painless mass | |||
| complications = Rarely malignant transformation | |||
| onset = Typically in adults | |||
| duration = Indefinite, unless surgically removed | |||
| types = Renal oncocytoma, salivary gland oncocytoma | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = Age, smoking, radiation exposure | |||
| diagnosis = [[Histopathology]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Adenoma]], [[carcinoma]] | |||
| prevention = None known | |||
| treatment = Surgical excision | |||
| medication = None | |||
| prognosis = Excellent with surgical removal | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = Very rare | |||
}} | |||
'''Oncocytoma''' is a type of [[tumor]] that is typically benign and occurs in the [[kidney]], [[salivary glands]], and other organs. It is characterized by the presence of large cells, known as oncocytic cells, which have an abundance of [[mitochondria]]. | '''Oncocytoma''' is a type of [[tumor]] that is typically benign and occurs in the [[kidney]], [[salivary glands]], and other organs. It is characterized by the presence of large cells, known as oncocytic cells, which have an abundance of [[mitochondria]]. | ||
== Introduction == | |||
== | |||
Oncocytomas are rare and account for approximately 5% of all benign renal tumors. They are usually discovered incidentally during imaging studies for unrelated conditions. Oncocytomas are typically asymptomatic, but they can sometimes cause symptoms such as [[hematuria]] (blood in the urine), [[abdominal pain]], and a palpable mass. | Oncocytomas are rare and account for approximately 5% of all benign renal tumors. They are usually discovered incidentally during imaging studies for unrelated conditions. Oncocytomas are typically asymptomatic, but they can sometimes cause symptoms such as [[hematuria]] (blood in the urine), [[abdominal pain]], and a palpable mass. | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
The diagnosis of oncocytoma is usually made based on the results of imaging studies, such as [[ultrasound]], [[computed tomography (CT) scan]], or [[magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)]]. However, the definitive diagnosis can only be made by examining the tumor under a microscope after it has been removed during surgery. | The diagnosis of oncocytoma is usually made based on the results of imaging studies, such as [[ultrasound]], [[computed tomography (CT) scan]], or [[magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)]]. However, the definitive diagnosis can only be made by examining the tumor under a microscope after it has been removed during surgery. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment for oncocytoma depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. In many cases, the tumor can be removed surgically. If the tumor is small and not causing any symptoms, it may be monitored with regular imaging studies to ensure that it is not growing or causing problems. | The treatment for oncocytoma depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. In many cases, the tumor can be removed surgically. If the tumor is small and not causing any symptoms, it may be monitored with regular imaging studies to ensure that it is not growing or causing problems. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for patients with oncocytoma is generally good, as these tumors are usually benign and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, in rare cases, oncocytomas can become malignant and spread to other organs. | The prognosis for patients with oncocytoma is generally good, as these tumors are usually benign and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, in rare cases, oncocytomas can become malignant and spread to other organs. | ||
==Gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Renal_oncocytoma3.jpg|Renal Oncocytoma | |||
File:Renal_oncocytoma4.jpg|Renal Oncocytoma | |||
File:Renal_oncocytoma.jpg|Renal Oncocytoma | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Renal cell carcinoma]] | * [[Renal cell carcinoma]] | ||
* [[Kidney cancer]] | * [[Kidney cancer]] | ||
* [[Benign tumor]] | * [[Benign tumor]] | ||
* [[Malignant tumor]] | * [[Malignant tumor]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Oncology]] | [[Category:Oncology]] | ||
[[Category:Pathology]] | [[Category:Pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Urology]] | [[Category:Urology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:00, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Oncocytoma | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Oncocytic adenoma |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, may present as a painless mass |
| Complications | Rarely malignant transformation |
| Onset | Typically in adults |
| Duration | Indefinite, unless surgically removed |
| Types | Renal oncocytoma, salivary gland oncocytoma |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | Age, smoking, radiation exposure |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Adenoma, carcinoma |
| Prevention | None known |
| Treatment | Surgical excision |
| Medication | None |
| Prognosis | Excellent with surgical removal |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | Very rare |
Oncocytoma is a type of tumor that is typically benign and occurs in the kidney, salivary glands, and other organs. It is characterized by the presence of large cells, known as oncocytic cells, which have an abundance of mitochondria.
Introduction[edit]
Oncocytomas are rare and account for approximately 5% of all benign renal tumors. They are usually discovered incidentally during imaging studies for unrelated conditions. Oncocytomas are typically asymptomatic, but they can sometimes cause symptoms such as hematuria (blood in the urine), abdominal pain, and a palpable mass.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of oncocytoma is usually made based on the results of imaging studies, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the definitive diagnosis can only be made by examining the tumor under a microscope after it has been removed during surgery.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment for oncocytoma depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. In many cases, the tumor can be removed surgically. If the tumor is small and not causing any symptoms, it may be monitored with regular imaging studies to ensure that it is not growing or causing problems.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for patients with oncocytoma is generally good, as these tumors are usually benign and do not spread to other parts of the body. However, in rare cases, oncocytomas can become malignant and spread to other organs.
Gallery[edit]
-
Renal Oncocytoma
-
Renal Oncocytoma
-
Renal Oncocytoma
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />