Fatigue: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Fatigue, | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
=== | | name = Fatigue | ||
| image = [[File:Cfs_woman_sketch.jpg|250px]] | |||
Fatigue | | caption = Sketch of a woman experiencing fatigue | ||
| field = [[Internal medicine]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Tiredness]], [[exhaustion]], [[lack of energy]] | |||
| complications = [[Depression (mood)|Depression]], [[anxiety]], [[reduced quality of life]] | |||
| onset = Can be [[acute (medicine)|acute]] or [[chronic (medicine)|chronic]] | |||
| duration = Varies; can be [[short-term]] or [[long-term]] | |||
| causes = [[Sleep deprivation]], [[stress (biology)|stress]], [[medical conditions]] such as [[anemia]], [[hypothyroidism]], [[chronic fatigue syndrome]] | |||
| risks = [[Poor diet]], [[sedentary lifestyle]], [[mental health disorders]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Clinical assessment]], [[blood tests]], [[sleep studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Depression (mood)|Depression]], [[sleep apnea]], [[anemia]], [[hypothyroidism]] | |||
| treatment = [[Lifestyle changes]], [[cognitive behavioral therapy]], [[medication]] | |||
| medication = [[Antidepressants]], [[stimulants]] | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
| deaths = Rarely directly fatal | |||
}} | |||
== Fatigue == | |||
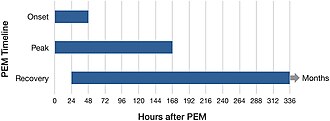
[[File:Timeframe_of_PEM_from_daily_activities.jpg|left|thumb|Diagram illustrating the timeframe of post-exertional malaise from daily activities.]] | |||
* [[ | '''Fatigue''' is a common symptom experienced by individuals across various conditions and is characterized by a persistent feeling of tiredness or exhaustion. It can be both a physical and mental state, affecting a person's ability to perform daily activities effectively. | ||
== Causes of Fatigue == | |||
Fatigue can result from numerous factors, including: | |||
* Chronic | * [[Sleep disorders]] such as [[insomnia]] or [[sleep apnea]]. | ||
* [[Chronic illnesses]] like [[chronic fatigue syndrome]] (CFS), [[fibromyalgia]], and [[multiple sclerosis]]. | |||
* [[Mental health]] issues, including [[depression]] and [[anxiety]]. | |||
* [[ | * [[Lifestyle factors]] such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and excessive stress. | ||
* [[Medications]] that have fatigue as a side effect. | |||
== Symptoms == | |||
The primary symptom of fatigue is a persistent feeling of tiredness that does not improve with rest. Other symptoms may include: | |||
* Difficulty concentrating or [[cognitive impairment]]. | |||
* [[Muscle weakness]] or soreness. | |||
* [[Headaches]]. | |||
* [[Dizziness]] or lightheadedness. | |||
* Irritability or mood changes. | |||
== Diagnosis == | |||
* | Diagnosing fatigue involves a comprehensive evaluation to determine the underlying cause. This may include: | ||
* | * A detailed medical history and physical examination. | ||
* [[Blood tests]] to check for [[anemia]], [[thyroid function]], and other potential causes. | |||
== | * [[Sleep studies]] to identify sleep disorders. | ||
* [[Psychological assessments]] to evaluate mental health conditions. | |||
* | == Management == | ||
* | Managing fatigue typically involves addressing the underlying cause. General strategies include: | ||
* | * Improving [[sleep hygiene]] and ensuring adequate rest. | ||
* Engaging in regular [[physical activity]] tailored to the individual's capabilities. | |||
* Managing stress through [[relaxation techniques]] and [[counseling]]. | |||
* Adjusting medications if they contribute to fatigue. | |||
Diagnosing fatigue involves a comprehensive | * Nutritional support and [[dietary changes]]. | ||
== See also == | |||
* | * [[Chronic fatigue syndrome]] | ||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
== | |||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
== See | |||
* [[Sleep disorders]] | * [[Sleep disorders]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Depression]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Fibromyalgia]] | ||
{{Medical symptoms}} | |||
{{ | |||
[[Category:Symptoms]] | [[Category:Symptoms]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:30, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Fatigue | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Tiredness, exhaustion, lack of energy |
| Complications | Depression, anxiety, reduced quality of life |
| Onset | Can be acute or chronic |
| Duration | Varies; can be short-term or long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Sleep deprivation, stress, medical conditions such as anemia, hypothyroidism, chronic fatigue syndrome |
| Risks | Poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, mental health disorders |
| Diagnosis | Clinical assessment, blood tests, sleep studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Depression, sleep apnea, anemia, hypothyroidism |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Lifestyle changes, cognitive behavioral therapy, medication |
| Medication | Antidepressants, stimulants |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Rarely directly fatal |
Fatigue[edit]
Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by individuals across various conditions and is characterized by a persistent feeling of tiredness or exhaustion. It can be both a physical and mental state, affecting a person's ability to perform daily activities effectively.
Causes of Fatigue[edit]
Fatigue can result from numerous factors, including:
- Sleep disorders such as insomnia or sleep apnea.
- Chronic illnesses like chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), fibromyalgia, and multiple sclerosis.
- Mental health issues, including depression and anxiety.
- Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and excessive stress.
- Medications that have fatigue as a side effect.
Symptoms[edit]
The primary symptom of fatigue is a persistent feeling of tiredness that does not improve with rest. Other symptoms may include:
- Difficulty concentrating or cognitive impairment.
- Muscle weakness or soreness.
- Headaches.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Irritability or mood changes.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosing fatigue involves a comprehensive evaluation to determine the underlying cause. This may include:
- A detailed medical history and physical examination.
- Blood tests to check for anemia, thyroid function, and other potential causes.
- Sleep studies to identify sleep disorders.
- Psychological assessments to evaluate mental health conditions.
Management[edit]
Managing fatigue typically involves addressing the underlying cause. General strategies include:
- Improving sleep hygiene and ensuring adequate rest.
- Engaging in regular physical activity tailored to the individual's capabilities.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques and counseling.
- Adjusting medications if they contribute to fatigue.
- Nutritional support and dietary changes.