Ameloblastic fibroma: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Ameloblastic fibroma | |||
| image = [[File:Enamelmineralization11-17-05.jpg|250px]] | |||
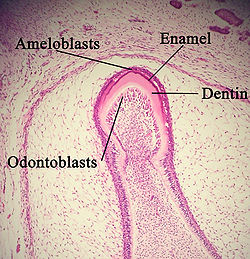
| caption = Histological image of ameloblastic fibroma | |||
| field = [[Oral and maxillofacial pathology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| pronunciation = | |||
| specialty = [[Dentistry]], [[Oral and maxillofacial surgery]] | |||
| symptoms = Swelling, pain, delayed tooth eruption | |||
| onset = Usually in the first two decades of life | |||
| duration = | |||
| types = | |||
| causes = Unknown | |||
| risks = | |||
| diagnosis = [[Histopathology]], [[Radiography]] | |||
| differential = [[Ameloblastoma]], [[Odontogenic myxoma]], [[Odontoma]] | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = Surgical excision | |||
| medication = | |||
| prognosis = Good with complete excision | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
| deaths = | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A rare benign odontogenic tumor}} | {{Short description|A rare benign odontogenic tumor}} | ||
== Ameloblastic Fibroma == | == Ameloblastic Fibroma == | ||
[[File:Enamelmineralization11-17-05.jpg|Enamel mineralization process|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Enamelmineralization11-17-05.jpg|Enamel mineralization process|thumb| | |||
'''Ameloblastic fibroma''' is a rare, benign [[odontogenic tumor]] that arises from the [[odontogenic epithelium]] and the [[mesenchymal]] tissue of the [[tooth germ]]. It is characterized by the proliferation of both epithelial and mesenchymal components, which distinguishes it from other odontogenic tumors. | '''Ameloblastic fibroma''' is a rare, benign [[odontogenic tumor]] that arises from the [[odontogenic epithelium]] and the [[mesenchymal]] tissue of the [[tooth germ]]. It is characterized by the proliferation of both epithelial and mesenchymal components, which distinguishes it from other odontogenic tumors. | ||
== Clinical Presentation == | == Clinical Presentation == | ||
Ameloblastic fibromas typically present as a painless swelling in the jaw, often discovered incidentally on radiographs. They are most commonly found in the posterior region of the [[mandible]], although they can also occur in the [[maxilla]]. The condition is more prevalent in children and young adults, with a slight male predominance. | Ameloblastic fibromas typically present as a painless swelling in the jaw, often discovered incidentally on radiographs. They are most commonly found in the posterior region of the [[mandible]], although they can also occur in the [[maxilla]]. The condition is more prevalent in children and young adults, with a slight male predominance. | ||
== Radiographic Features == | == Radiographic Features == | ||
On radiographic examination, ameloblastic fibromas appear as well-defined radiolucent lesions. They may be unilocular or multilocular, and the borders are often corticated. The lesion can cause displacement of adjacent teeth and may be associated with an unerupted tooth. | On radiographic examination, ameloblastic fibromas appear as well-defined radiolucent lesions. They may be unilocular or multilocular, and the borders are often corticated. The lesion can cause displacement of adjacent teeth and may be associated with an unerupted tooth. | ||
== Histopathology == | == Histopathology == | ||
Histologically, ameloblastic fibromas consist of strands and islands of odontogenic epithelium resembling the [[ameloblastoma]], set within a cellular mesenchymal stroma that resembles the dental papilla. The epithelial component may form structures similar to the enamel organ, but without enamel formation. | Histologically, ameloblastic fibromas consist of strands and islands of odontogenic epithelium resembling the [[ameloblastoma]], set within a cellular mesenchymal stroma that resembles the dental papilla. The epithelial component may form structures similar to the enamel organ, but without enamel formation. | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment of choice for ameloblastic fibroma is surgical excision. Due to the potential for recurrence, complete removal with a margin of healthy tissue is recommended. In some cases, more aggressive surgical approaches may be necessary to prevent recurrence. | The treatment of choice for ameloblastic fibroma is surgical excision. Due to the potential for recurrence, complete removal with a margin of healthy tissue is recommended. In some cases, more aggressive surgical approaches may be necessary to prevent recurrence. | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis for ameloblastic fibroma is generally good, with a low rate of malignant transformation. However, there is a risk of recurrence if the lesion is not completely excised. Long-term follow-up is advised to monitor for any signs of recurrence or malignant transformation into an [[ameloblastic fibrosarcoma]]. | The prognosis for ameloblastic fibroma is generally good, with a low rate of malignant transformation. However, there is a risk of recurrence if the lesion is not completely excised. Long-term follow-up is advised to monitor for any signs of recurrence or malignant transformation into an [[ameloblastic fibrosarcoma]]. | ||
== See Also == | |||
== | |||
* [[Odontogenic tumor]] | * [[Odontogenic tumor]] | ||
* [[Ameloblastoma]] | * [[Ameloblastoma]] | ||
* [[Odontogenic myxoma]] | * [[Odontogenic myxoma]] | ||
* [[Dental anatomy]] | * [[Dental anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Odontogenic tumors]] | [[Category:Odontogenic tumors]] | ||
[[Category:Benign neoplasms]] | [[Category:Benign neoplasms]] | ||
[[Category:Oral pathology]] | [[Category:Oral pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:33, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ameloblastic fibroma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dentistry, Oral and maxillofacial surgery |
| Symptoms | Swelling, pain, delayed tooth eruption |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Usually in the first two decades of life |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Histopathology, Radiography |
| Differential diagnosis | Ameloblastoma, Odontogenic myxoma, Odontoma |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgical excision |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Good with complete excision |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
A rare benign odontogenic tumor
Ameloblastic Fibroma[edit]

Ameloblastic fibroma is a rare, benign odontogenic tumor that arises from the odontogenic epithelium and the mesenchymal tissue of the tooth germ. It is characterized by the proliferation of both epithelial and mesenchymal components, which distinguishes it from other odontogenic tumors.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Ameloblastic fibromas typically present as a painless swelling in the jaw, often discovered incidentally on radiographs. They are most commonly found in the posterior region of the mandible, although they can also occur in the maxilla. The condition is more prevalent in children and young adults, with a slight male predominance.
Radiographic Features[edit]
On radiographic examination, ameloblastic fibromas appear as well-defined radiolucent lesions. They may be unilocular or multilocular, and the borders are often corticated. The lesion can cause displacement of adjacent teeth and may be associated with an unerupted tooth.
Histopathology[edit]
Histologically, ameloblastic fibromas consist of strands and islands of odontogenic epithelium resembling the ameloblastoma, set within a cellular mesenchymal stroma that resembles the dental papilla. The epithelial component may form structures similar to the enamel organ, but without enamel formation.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of choice for ameloblastic fibroma is surgical excision. Due to the potential for recurrence, complete removal with a margin of healthy tissue is recommended. In some cases, more aggressive surgical approaches may be necessary to prevent recurrence.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for ameloblastic fibroma is generally good, with a low rate of malignant transformation. However, there is a risk of recurrence if the lesion is not completely excised. Long-term follow-up is advised to monitor for any signs of recurrence or malignant transformation into an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma.