Levomepromazine: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{Pharma-stub}} | {{Pharma-stub}} | ||
{{Medicine-stub}} | {{Medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
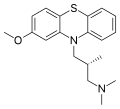
File:Levomepromazine.svg|Levomepromazine | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:34, 17 March 2025
Levomepromazine (also known as Methotrimeprazine) is a pharmacological agent classified under the category of phenothiazine derivatives. It is primarily used in the field of medicine as an antipsychotic and analgesic drug.
History[edit]
Levomepromazine was first synthesized in the 1950s as part of the development of the phenothiazine class of drugs. It was initially used as an antipsychotic, but its use has since expanded to include the treatment of nausea and vomiting, as well as severe, chronic pain.
Pharmacology[edit]
Levomepromazine is a dopamine antagonist, which means it works by blocking the action of dopamine, a neurotransmitter in the brain. It also has anticholinergic, antihistamine, and antiadrenergic properties, which contribute to its various therapeutic effects and side effects.
Medical Uses[edit]
Levomepromazine is used in the treatment of a variety of conditions. These include:
- Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders
- Nausea and vomiting, particularly when caused by chemotherapy or radiotherapy
- Severe, chronic pain, particularly when other analgesics are not effective
Side Effects[edit]
Like all medications, Levomepromazine can cause side effects. These can include drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, and constipation. In rare cases, it can cause serious side effects such as tardive dyskinesia and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
-
Levomepromazine