Butamben: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|A local anesthetic used in medical procedures}} | |||
{{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | |||
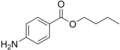
'''Butamben''' is a local anesthetic commonly used in medical procedures to provide temporary relief from pain. It is an ester of [[p-aminobenzoic acid]] and is known for its effectiveness in topical applications. Butamben is often used in combination with other anesthetics to enhance its efficacy. | |||
Butamben | |||
== | ==Chemical Properties== | ||
Butamben is | Butamben is chemically classified as an ester anesthetic. Its chemical formula is C11H15NO2, and it has a molecular weight of 193.24 g/mol. The compound is a white, crystalline powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and ether. | ||
== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Butamben works by blocking [[sodium channels]] in the neuronal cell membrane, which inhibits the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses. This action results in a loss of sensation in the area where the anesthetic is applied. By preventing the transmission of pain signals to the brain, butamben provides effective local anesthesia. | |||
==Uses== | |||
Butamben is primarily used in topical formulations for the relief of pain associated with minor skin irritations, burns, and insect bites. It is also used in some dental procedures to numb the mucous membranes of the mouth. In combination with other anesthetics, butamben can be used for more extensive procedures requiring deeper anesthesia. | |||
== | ==Administration== | ||
Butamben | Butamben is typically administered as a topical cream or ointment. It is applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes in the area requiring anesthesia. The onset of action is usually rapid, providing quick relief from pain. | ||
== | ==Side Effects== | ||
Common side effects of butamben include localized redness, itching, and irritation at the site of application. In rare cases, patients may experience allergic reactions, which can manifest as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing. It is important to use butamben as directed and to consult a healthcare professional if any adverse reactions occur. | |||
== | ==Precautions== | ||
Patients with a known allergy to ester-type anesthetics or [[p-aminobenzoic acid]] should avoid using butamben. It is also important to avoid applying the anesthetic to large areas of the body or to broken skin, as this can increase the risk of systemic absorption and toxicity. | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
* [[Local anesthetic]] | |||
* [[p-Aminobenzoic acid]] | |||
* [[Sodium channel]] | |||
* [[Topical anesthetic]] | |||
[[Category:Local anesthetics]] | [[Category:Local anesthetics]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Anesthesiology]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Medical treatments]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:butamben.png|Butamben | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 00:55, 20 February 2025
A local anesthetic used in medical procedures
Butamben is a local anesthetic commonly used in medical procedures to provide temporary relief from pain. It is an ester of p-aminobenzoic acid and is known for its effectiveness in topical applications. Butamben is often used in combination with other anesthetics to enhance its efficacy.
Chemical Properties[edit]
Butamben is chemically classified as an ester anesthetic. Its chemical formula is C11H15NO2, and it has a molecular weight of 193.24 g/mol. The compound is a white, crystalline powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and ether.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Butamben works by blocking sodium channels in the neuronal cell membrane, which inhibits the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses. This action results in a loss of sensation in the area where the anesthetic is applied. By preventing the transmission of pain signals to the brain, butamben provides effective local anesthesia.
Uses[edit]
Butamben is primarily used in topical formulations for the relief of pain associated with minor skin irritations, burns, and insect bites. It is also used in some dental procedures to numb the mucous membranes of the mouth. In combination with other anesthetics, butamben can be used for more extensive procedures requiring deeper anesthesia.
Administration[edit]
Butamben is typically administered as a topical cream or ointment. It is applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes in the area requiring anesthesia. The onset of action is usually rapid, providing quick relief from pain.
Side Effects[edit]
Common side effects of butamben include localized redness, itching, and irritation at the site of application. In rare cases, patients may experience allergic reactions, which can manifest as rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing. It is important to use butamben as directed and to consult a healthcare professional if any adverse reactions occur.
Precautions[edit]
Patients with a known allergy to ester-type anesthetics or p-aminobenzoic acid should avoid using butamben. It is also important to avoid applying the anesthetic to large areas of the body or to broken skin, as this can increase the risk of systemic absorption and toxicity.
Related Pages[edit]
-
Butamben