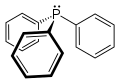Triphenylphosphine: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An organophosphorus compound used in organic synthesis}} | |||
{{Chembox | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477239679 | |||
| ImageFile = Triphenylphosphine-2D-skeletal_Smokefoot-style.svg | |||
| ImageSize = 200px | |||
| ImageAlt = Skeletal formula of triphenylphosphine | |||
| IUPACName = Triphenylphosphane | |||
| OtherNames = TPP, PPh_ | |||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| CASNo = 603-35-0 | |||
| PubChem = 1038 | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 1010 | |||
| UNII = 0F8P2QJZ0T | |||
| ChEBI = 30089 | |||
| ChEMBL = 1405 | |||
| SMILES = c1ccc(cc1)P(c2ccccc2)c3ccccc3 | |||
| InChI = 1S/C18H15P/c1-4-10-16(11-5-1)19(17-12-6-2-7-13-17)18-14-8-3-9-15-18/h1-15H | |||
| InChIKey = RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
== | '''Triphenylphosphine''' (often abbreviated as '''TPP''' or '''PPh_''') is an [[organophosphorus compound]] with the formula '''P(C_H_)_'''. It is a common [[reagent]] in [[organic synthesis]] and is used as a [[ligand]] in [[coordination chemistry]]. | ||
Triphenylphosphine is a white | |||
==Structure and properties== | |||
Triphenylphosphine is a [[white]] [[crystalline]] solid at room temperature. It is soluble in [[organic solvents]] such as [[benzene]], [[diethyl ether]], and [[chloroform]]. The compound is characterized by a [[trigonal pyramidal]] geometry around the phosphorus atom, with three phenyl groups attached. | |||
==Synthesis== | ==Synthesis== | ||
Triphenylphosphine is typically synthesized by the reaction of [[phosphorus trichloride]] with [[phenylmagnesium bromide]] or [[phenyl lithium]]. The reaction proceeds as follows: | |||
<math>\text{PCl}_3 + 3 \text{C}_6\text{H}_5\text{MgBr} \rightarrow \text{P}(\text{C}_6\text{H}_5)_3 + 3 \text{MgBrCl}</math> | |||
==Applications== | ==Applications== | ||
Triphenylphosphine | ===In organic synthesis=== | ||
Triphenylphosphine is widely used in organic synthesis. It is a key component in the [[Wittig reaction]], which is used to convert [[carbonyl compounds]] into [[alkenes]]. The reaction involves the formation of a [[phosphonium ylide]] intermediate. | |||
===Deoxygenation reactions=== | |||
Triphenylphosphine is also used in deoxygenation reactions, such as the conversion of [[amine oxides]] to [[amines]]. This reaction is depicted in the following image: | |||
[[File:Deoxygenation_of_an_aromatic_amine_oxide_using_triphenylphosphine.png|thumb|center|400px|Deoxygenation of an aromatic amine oxide using triphenylphosphine]] | |||
===As a ligand=== | |||
In coordination chemistry, triphenylphosphine acts as a [[ligand]] that can stabilize [[transition metal]] complexes. It is often used in [[homogeneous catalysis]], such as in the [[hydroformylation]] of [[olefins]]. | |||
==Derivatives== | |||
Triphenylphosphine can be modified to form various derivatives, such as [[TPPTS]] (triphenylphosphine-3,3',3''-trisulfonate), which is used in [[aqueous]] [[catalysis]]. | |||
[[File:TPPTS.png|thumb|right|200px|Structure of TPPTS]] | |||
==Safety== | ==Safety== | ||
Triphenylphosphine is generally considered to be of low toxicity, but it | Triphenylphosphine is generally considered to be of low toxicity, but it can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Proper handling and storage are recommended to avoid exposure. | ||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Phosphine]] | * [[Phosphine]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Wittig reaction]] | ||
* [[Coordination chemistry]] | * [[Coordination chemistry]] | ||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Organophosphorus compounds]] | [[Category:Organophosphorus compounds]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Reagents for organic chemistry]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Triphenylphosphine-2D-skeletal_Smokefoot-style.svg|Triphenylphosphine 2D skeletal structure | |||
File:Deoxygenation_of_an_aromatic_amine_oxide_using_triphenylphosphine.png|Deoxygenation of an aromatic amine oxide using triphenylphosphine | |||
File:TPPTS.png|TPPTS | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:21, 18 February 2025
An organophosphorus compound used in organic synthesis
| Chemical Compound | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molar Mass | |
| Appearance | |
| Density | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Pictograms | [[File:|50px]] |
| GHS Signal Word | |
| GHS Hazard Statements | |
| NFPA 704 | [[File:|50px]] |
| References | |
Triphenylphosphine (often abbreviated as TPP or PPh_) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C_H_)_. It is a common reagent in organic synthesis and is used as a ligand in coordination chemistry.
Structure and properties[edit]
Triphenylphosphine is a white crystalline solid at room temperature. It is soluble in organic solvents such as benzene, diethyl ether, and chloroform. The compound is characterized by a trigonal pyramidal geometry around the phosphorus atom, with three phenyl groups attached.
Synthesis[edit]
Triphenylphosphine is typically synthesized by the reaction of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyl lithium. The reaction proceeds as follows:
Applications[edit]
In organic synthesis[edit]
Triphenylphosphine is widely used in organic synthesis. It is a key component in the Wittig reaction, which is used to convert carbonyl compounds into alkenes. The reaction involves the formation of a phosphonium ylide intermediate.
Deoxygenation reactions[edit]
Triphenylphosphine is also used in deoxygenation reactions, such as the conversion of amine oxides to amines. This reaction is depicted in the following image:

As a ligand[edit]
In coordination chemistry, triphenylphosphine acts as a ligand that can stabilize transition metal complexes. It is often used in homogeneous catalysis, such as in the hydroformylation of olefins.
Derivatives[edit]
Triphenylphosphine can be modified to form various derivatives, such as TPPTS (triphenylphosphine-3,3',3-trisulfonate), which is used in aqueous catalysis.

Safety[edit]
Triphenylphosphine is generally considered to be of low toxicity, but it can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. Proper handling and storage are recommended to avoid exposure.
Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
-
Triphenylphosphine 2D skeletal structure
-
Deoxygenation of an aromatic amine oxide using triphenylphosphine
-
TPPTS