Ubenimex: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|An aminopeptidase inhibitor used in cancer research}} | |||
{{Drugbox | |||
| verifiedrevid = 477241123 | |||
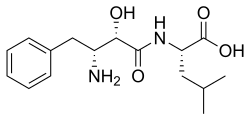
| IUPAC_name = (2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanoyl-L-leucine | |||
| image = Ubenimex2DCSD.svg | |||
| image2 = Bestatin.jpg | |||
}} | |||
'''Ubenimex''', also known as '''bestatin''', is a potent inhibitor of aminopeptidases, a class of enzymes that play a role in the degradation of proteins. It is primarily used in research settings to study its effects on cancer and immune system modulation. | |||
Ubenimex is | |||
== | ==Discovery and Development== | ||
Ubenimex | Ubenimex was first isolated from the culture broth of the bacterium ''[[Streptomyces olivoreticuli]]''. The compound was identified as a potent inhibitor of aminopeptidase B and leucine aminopeptidase, enzymes involved in protein metabolism. Its discovery has led to extensive research into its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in oncology. | ||
== | ==Mechanism of Action== | ||
Ubenimex functions by inhibiting aminopeptidases, which are enzymes that remove amino acids from the amino terminus of proteins and peptides. By inhibiting these enzymes, ubenimex can interfere with the breakdown of proteins, potentially affecting various cellular processes. This mechanism is thought to contribute to its effects on tumor growth and immune response. | |||
== | ==Clinical Applications== | ||
While ubenimex has shown promise in preclinical studies, its clinical applications are still under investigation. It has been studied for its potential use in treating various types of cancer, including [[leukemia]] and [[lung cancer]]. Additionally, ubenimex has been explored for its immunomodulatory effects, which could make it useful in treating autoimmune diseases and enhancing immune responses. | |||
== | ==Research and Studies== | ||
Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ubenimex in different therapeutic contexts. In cancer research, it has been tested in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents to assess its ability to enhance treatment outcomes. Research has also focused on its role in modulating the immune system, with some studies suggesting it may enhance the activity of [[natural killer cells]] and [[T cells]]. | |||
[[Category: | ==Related Pages== | ||
[[Category: | * [[Aminopeptidase]] | ||
[[Category: | * [[Cancer research]] | ||
* [[Immunotherapy]] | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Enzyme inhibitors]] | |||
[[Category:Experimental cancer drugs]] | |||
[[Category:Immunomodulating drugs]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ubenimex2DCSD.svg | |||
File:Bestatin.jpg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:49, 17 February 2025
An aminopeptidase inhibitor used in cancer research
| Ubenimex | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | |
| Elimination half-life | |
| Excretion | |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
Ubenimex, also known as bestatin, is a potent inhibitor of aminopeptidases, a class of enzymes that play a role in the degradation of proteins. It is primarily used in research settings to study its effects on cancer and immune system modulation.
Discovery and Development[edit]
Ubenimex was first isolated from the culture broth of the bacterium Streptomyces olivoreticuli. The compound was identified as a potent inhibitor of aminopeptidase B and leucine aminopeptidase, enzymes involved in protein metabolism. Its discovery has led to extensive research into its potential therapeutic applications, particularly in oncology.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Ubenimex functions by inhibiting aminopeptidases, which are enzymes that remove amino acids from the amino terminus of proteins and peptides. By inhibiting these enzymes, ubenimex can interfere with the breakdown of proteins, potentially affecting various cellular processes. This mechanism is thought to contribute to its effects on tumor growth and immune response.
Clinical Applications[edit]
While ubenimex has shown promise in preclinical studies, its clinical applications are still under investigation. It has been studied for its potential use in treating various types of cancer, including leukemia and lung cancer. Additionally, ubenimex has been explored for its immunomodulatory effects, which could make it useful in treating autoimmune diseases and enhancing immune responses.
Research and Studies[edit]
Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ubenimex in different therapeutic contexts. In cancer research, it has been tested in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents to assess its ability to enhance treatment outcomes. Research has also focused on its role in modulating the immune system, with some studies suggesting it may enhance the activity of natural killer cells and T cells.
Related Pages[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
