Keratin 8: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Keratin 8}} | |||
'''Keratin 8''' is a type of [[intermediate filament]] protein that is primarily found in the [[epithelial cells]] of the [[gastrointestinal tract]], [[liver]], and other [[internal organs]]. It is part of the [[keratin]] family, which is a group of fibrous structural proteins that are key components of the [[cytoskeleton]] in epithelial cells. | |||
Keratin 8 is a type of intermediate filament protein, | |||
== | ==Structure== | ||
Keratin 8 | [[File:Cytokeratin_8.jpg|thumb|right|Keratin 8 structure]] | ||
Keratin 8 is a type II keratin, which means it is a basic or neutral keratin. It forms heterodimers with type I keratins, such as [[keratin 18]], to create the intermediate filament network within cells. This network provides structural support and helps maintain cell integrity. | |||
== | ==Function== | ||
Keratin 8 plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural stability of epithelial cells. It is involved in protecting cells from mechanical and non-mechanical stress. Additionally, keratin 8 is implicated in various cellular processes, including [[apoptosis]], [[cell signaling]], and [[cell cycle]] regulation. | |||
== | ==Expression== | ||
Keratin 8 is predominantly expressed in simple epithelial tissues. It is a marker for simple epithelia and is often used in [[immunohistochemistry]] to identify epithelial cells in tissue samples. Its expression is regulated by various factors, including [[cytokines]] and [[growth factors]]. | |||
==Clinical Significance== | |||
Mutations in the gene encoding keratin 8 can lead to a variety of [[diseases]], particularly those affecting the liver. For example, certain mutations are associated with [[liver cirrhosis]] and [[inflammatory bowel disease]]. Keratin 8 is also studied in the context of [[cancer]], as its expression levels can be altered in [[tumor]] cells. | |||
==Research== | |||
Research on keratin 8 continues to explore its role in [[disease pathogenesis]] and its potential as a [[biomarker]] for various conditions. Studies are also investigating the therapeutic potential of targeting keratin 8 in disease treatment. | |||
==Related pages== | |||
* [[Keratin 18]] | * [[Keratin 18]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Intermediate filament]] | ||
* [[Epithelial cell]] | |||
* [[Cytoskeleton]] | * [[Cytoskeleton]] | ||
[[Category:Keratins]] | |||
[[Category:Proteins]] | [[Category:Proteins]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Cell biology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:01, 13 February 2025
Keratin 8 is a type of intermediate filament protein that is primarily found in the epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and other internal organs. It is part of the keratin family, which is a group of fibrous structural proteins that are key components of the cytoskeleton in epithelial cells.
Structure[edit]
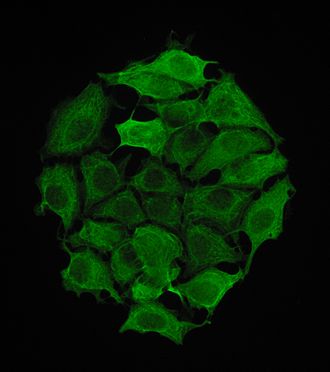
Keratin 8 is a type II keratin, which means it is a basic or neutral keratin. It forms heterodimers with type I keratins, such as keratin 18, to create the intermediate filament network within cells. This network provides structural support and helps maintain cell integrity.
Function[edit]
Keratin 8 plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural stability of epithelial cells. It is involved in protecting cells from mechanical and non-mechanical stress. Additionally, keratin 8 is implicated in various cellular processes, including apoptosis, cell signaling, and cell cycle regulation.
Expression[edit]
Keratin 8 is predominantly expressed in simple epithelial tissues. It is a marker for simple epithelia and is often used in immunohistochemistry to identify epithelial cells in tissue samples. Its expression is regulated by various factors, including cytokines and growth factors.
Clinical Significance[edit]
Mutations in the gene encoding keratin 8 can lead to a variety of diseases, particularly those affecting the liver. For example, certain mutations are associated with liver cirrhosis and inflammatory bowel disease. Keratin 8 is also studied in the context of cancer, as its expression levels can be altered in tumor cells.
Research[edit]
Research on keratin 8 continues to explore its role in disease pathogenesis and its potential as a biomarker for various conditions. Studies are also investigating the therapeutic potential of targeting keratin 8 in disease treatment.