Standard score
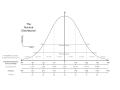
Standard score is a statistical measure that quantifies the relative position of a specific score or measurement within a set of scores. The standard score is calculated by subtracting the mean of the dataset from the score in question and then dividing the result by the standard deviation of the dataset. This process is known as standardization or z-score normalization. The formula for calculating a standard score is:
\[ z = \frac{(X - \mu)}{\sigma} \]
where:
- \(X\) is the score in question,
- \(\mu\) is the mean of the dataset,
- \(\sigma\) is the standard deviation of the dataset.
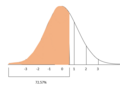
Standard scores are dimensionless and provide a way to compare scores from different distributions or datasets by converting them into a common scale. A standard score of 0 indicates that the score is exactly at the mean of the distribution, while a positive or negative standard score indicates a score above or below the mean, respectively.
Importance of Standard Scores[edit]
Standard scores are widely used in various fields, including psychology, education, medicine, and research, for purposes such as:
- Comparing individual scores across different tests or assessments.
- Identifying and analyzing outliers within datasets.
- Facilitating the calculation of probabilities and the identification of percentile ranks.
- Standardizing scores to enable the comparison of data from different sources or distributions.
Types of Standard Scores[edit]
There are several types of standard scores, each with its specific application and calculation method. These include:
- Z-score: The most common type of standard score, directly reflecting how many standard deviations an element is from the mean.
- T-score: A type of standard score with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of 10, often used in educational testing and psychological assessment.
- Stanine: A method of scaling scores on a nine-point standard scale with a mean of 5 and a standard deviation of approximately 2, used in educational assessment.
- Percentile rank: A score indicating the percentage of scores in its frequency distribution that are equal to or lower than it.
Applications[edit]
Standard scores are utilized in a variety of applications, including:
- In psychometrics for the normalization of test scores to facilitate comparison across different tests or populations.
- In finance, to assess the performance of financial instruments relative to a benchmark or mean performance.
- In healthcare, to standardize measurements of patient outcomes, facilitating comparison across different populations or treatment groups.
Limitations[edit]
While standard scores are a powerful tool for statistical analysis, they have limitations, including:
- They assume that the data follows a normal distribution, which may not always be the case.
- They can be influenced by outliers or extreme values, affecting the mean and standard deviation and, consequently, the standard scores.
- They do not provide information about the original scale or units of measurement, which can be critical in some analyses.
See Also[edit]

This article is a mathematics-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
-
Standard_score
-
Z score for Students A
-
Z score for Student B
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian