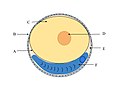
Yolk
Yolk is a component found in the eggs of many animal species. It serves as a primary source of nutrition for the developing embryo. The yolk is surrounded by the albumen, or egg white, and is separated from it by the vitelline membrane.
Composition[edit]
The yolk contains most of the egg's vitamins and minerals, proteins, and a significant portion of its fat. It is made up of approximately 50% water, 16% protein, 32% fat, and 2% vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates. The yolk also contains cholesterol, which has led to discussions about the health implications of consuming egg yolks.
Yolk in Different Species[edit]
The yolk's composition can vary significantly between different species. For example, the yolk of a chicken egg is different from that of a duck egg or a reptile egg. In some species, such as birds and reptiles, the yolk is a primary source of nourishment for the developing embryo. In others, such as mammals, the yolk is present but does not play a significant role in embryonic development.
Yolk Color[edit]
The color of the yolk can range from pale yellow to deep orange, depending on the diet of the animal. The color is primarily determined by the presence of carotenoids, which are pigments found in plants and algae. Animals that consume a diet rich in carotenoids will produce yolks with a deeper color.
Uses[edit]
Yolk is used in many culinary applications. It is a key ingredient in baking, where it can contribute to the texture, color, and flavor of baked goods. Yolk is also used in the production of mayonnaise, where it acts as an emulsifier to combine oil and vinegar.
Health Implications[edit]
The consumption of egg yolk has been a topic of debate due to its high cholesterol content. However, recent studies suggest that dietary cholesterol does not have a significant impact on blood cholesterol levels in most people. Instead, saturated and trans fats have a much greater effect on blood cholesterol levels.

-
Yolk
-
Fish Egg Diagram
-
Double and Single Yolk Hen Eggs
-
Egg and Maxi Egg
-
Egg and Maxi Egg
-
Egg with Two Yellows
-
Red Yolk
-
Pregnant Caridina multidentata in Captivity
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian