Wallerian degeneration

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Wallerian degeneration | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Loss of function in the affected nerve |
| Complications | Neuropathy, muscle atrophy |
| Onset | After nerve injury |
| Duration | Variable, depending on the extent of injury and regeneration |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Axonal injury |
| Risks | Trauma, surgery, ischemia |
| Diagnosis | Electromyography, nerve conduction study, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Axonal degeneration, demyelinating disease |
| Prevention | Protecting nerves from injury |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, occupational therapy, surgical repair |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on the extent of nerve damage and regeneration |
| Frequency | Common after nerve injuries |
| Deaths | N/A |
Wallerian Degeneration[edit]
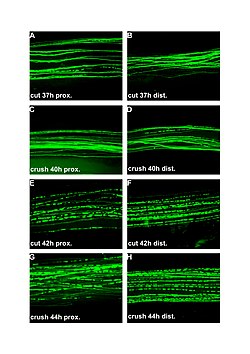
Wallerian degeneration is a process that occurs when a nerve fiber is cut or damaged. The part of the axon separated from the neuron's nucleus degenerates. This form of neural degeneration was first described by the British neurologist Augustus Waller in 1850.

Background and Discovery[edit]

- Historical Context
- Augustus Waller was the first to observe that the part of the axon separated from the neuron's cell body degenerates, a phenomenon now named after him.
- Definition
- Wallerian degeneration refers specifically to the degeneration of the distal part of an axon after injury, while the part of the axon still connected to the cell body typically survives.
Mechanism of Wallerian Degeneration[edit]
- Axonal Injury
- When an axon is damaged, the segment of the axon that is cut off from the cell body's metabolic support begins to swell and disintegrate. This process can be divided into several stages.
- Degenerative Process
- The degeneration includes the breakdown of the axonal membrane, the disintegration of the cytoskeleton, and the degradation of the myelin sheath by cells called macrophages.
Clinical Significance[edit]
- Neurological Implications
- Wallerian degeneration is a key component in nerve injuries and diseases. Understanding this process is important for treatments aimed at nerve regeneration.
- Regenerative Efforts
- Research into Wallerian degeneration has implications for spinal cord injury repair, peripheral neuropathies, and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Research and Future Directions[edit]
- Advances in Understanding
- Ongoing research is shedding light on the molecular mechanisms behind Wallerian degeneration, offering potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
- Potential Therapies
- Strategies to delay or inhibit Wallerian degeneration are considered potential therapeutic avenues for the treatment of various neurological disorders.
Augustus Waller and Historical Perspective[edit]
- Biography
- Augustus Waller was a prominent 19th-century physician and neuroanatomist whose work laid the foundation for the study of nerve degeneration and regeneration.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


