Viscoelasticity
A property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation
Viscoelasticity is a property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. This property is particularly important in the study of biological tissues, polymers, and other complex materials. Viscoelastic materials have the ability to dissipate energy, which is a key factor in their behavior under stress and strain.
Properties of Viscoelastic Materials[edit]
Viscoelastic materials are characterized by their time-dependent strain response to stress. This means that the deformation of the material is not only dependent on the applied stress but also on the duration for which the stress is applied. The key properties of viscoelastic materials include:
Creep[edit]
Creep is the tendency of a viscoelastic material to deform permanently under a constant load over time. When a constant stress is applied, the material will initially deform elastically, but over time, it will continue to deform at a decreasing rate.
Stress Relaxation[edit]
Stress relaxation is the decrease in stress experienced by a viscoelastic material when it is held at a constant strain. Over time, the material will adjust to the strain, resulting in a reduction of the internal stress.
Hysteresis[edit]
Hysteresis refers to the energy loss in a viscoelastic material when it is subjected to cyclic loading and unloading. This energy loss is due to the internal friction within the material, which causes the stress-strain curve to form a loop.
Dynamic Moduli[edit]
The dynamic moduli, including the storage modulus and the loss modulus, describe the material's response to oscillatory stress. The storage modulus represents the stored energy, while the loss modulus represents the energy dissipated as heat.
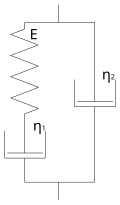
Mathematical Models[edit]
Several mathematical models are used to describe the behavior of viscoelastic materials. These models help in predicting the response of materials under various conditions.
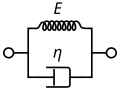
Maxwell Model[edit]
The Maxwell model represents a viscoelastic material as a combination of a spring and a dashpot in series. It is useful for modeling materials that exhibit stress relaxation.
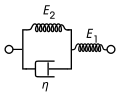
Kelvin-Voigt Model[edit]
The Kelvin-Voigt model consists of a spring and a dashpot in parallel. It is used to describe materials that exhibit creep behavior.
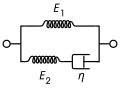
Standard Linear Solid Model[edit]
The standard linear solid model, also known as the Zener model, combines elements of both the Maxwell and Kelvin-Voigt models to provide a more comprehensive description of viscoelastic behavior.
Applications in Medicine[edit]
Viscoelasticity is a critical property in the field of medicine, particularly in the study of biomechanics and tissue engineering.
Biomechanics[edit]
In biomechanics, the viscoelastic properties of tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage are essential for understanding their function and response to mechanical loads. These properties influence how tissues absorb shock and distribute forces throughout the body.
Tissue Engineering[edit]
In tissue engineering, understanding the viscoelastic properties of scaffolds and biomaterials is crucial for designing materials that mimic the mechanical behavior of natural tissues. This knowledge helps in developing implants and prosthetics that integrate well with the body.
Related Pages[edit]
Viscoelasticity[edit]
-
Non-Newtonian fluid
-
Elastic vs. viscoelastic material
-
Comparison of three and four element models
-
Maxwell diagram
-
Kelvin-Voigt diagram
-
SLS
-
SLS2
-
Jeffreys rheological model
-
Burgers model 2
-
Burgers model
-
Weichert
-
Visco
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian