Ulegyria
A type of brain injury
Ulegyria is a form of brain injury characterized by scarring and atrophy of the cerebral cortex, particularly affecting the gyri. This condition is often associated with perinatal hypoxic-ischemic events, where the brain is deprived of adequate oxygen supply during birth.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Ulegyria results from a lack of oxygen (hypoxia) and blood flow (ischemia) to the brain, typically occurring around the time of birth. This leads to selective vulnerability of the cortical neurons, particularly in the depths of the sulci, resulting in a characteristic "mushroom-shaped" appearance of the gyri. The condition is often associated with cerebral palsy and other neurodevelopmental disorders.

Clinical Features[edit]
Individuals with ulegyria may present with a variety of neurological symptoms, including seizures, motor deficits, and cognitive impairments. The severity of symptoms can vary widely depending on the extent and location of the brain injury.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of ulegyria is typically made through neuroimaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can reveal the characteristic cortical scarring and atrophy. MRI may show the "mushroom-shaped" gyri and other structural abnormalities in the brain.

Treatment[edit]
There is no specific treatment for ulegyria, and management focuses on addressing the symptoms and complications associated with the condition. This may include antiepileptic drugs for seizure control, physical therapy for motor deficits, and educational interventions for cognitive impairments.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with ulegyria varies depending on the severity of the brain injury and the presence of associated conditions. Early intervention and supportive therapies can improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Related Conditions[edit]
Ulegyria is often discussed in the context of other conditions resulting from perinatal brain injury, such as polymicrogyria and periventricular leukomalacia.

Related pages[edit]
References[edit]
- Volpe, J. J. (2008). Neurology of the Newborn. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier.
- Barkovich, A. J. (2012). Pediatric Neuroimaging. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
-
Diagram of brain gyri and sulci
-
Arteries beneath the brain
-
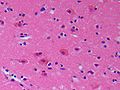
Histological image of acute stroke
-
Polymicrogyria with arrows indicating affected areas
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian