Sun




The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, with internal convective motion that generates a magnetic field via a dynamo process. The Sun is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. It provides the light and heat necessary for plants to perform photosynthesis, which is the basis of Earth's food chain and, by extension, the energy source for almost all life on the planet.
Structure[edit]
The Sun's structure can be divided into several layers: the core, the radiative zone, and the convective zone, followed by the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The core is where nuclear fusion occurs, converting hydrogen into helium and releasing vast amounts of energy. This energy then travels outward through the radiative and convective zones before reaching the surface and being emitted as sunlight.
Nuclear Fusion[edit]
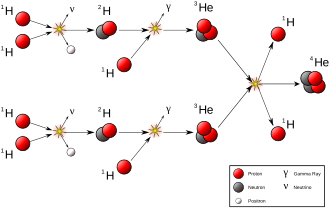
The process of nuclear fusion in the Sun's core produces not only light and heat but also solar neutrinos and small amounts of heavier elements. The primary reaction is the fusion of hydrogen into helium through the proton-proton chain reaction or the CNO cycle, depending on the region of the core.
Solar Activity[edit]
The Sun exhibits various forms of solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections. These phenomena are all manifestations of the Sun's magnetic field, which is generated by the flow of electrically conducting gases in its interior. Solar activity follows an approximately 11-year cycle known as the solar cycle.
Observation and Impact on Earth[edit]
The Sun has been observed by humans since prehistoric times and has played a crucial role in the development of many cultures and religions. In modern times, the study of the Sun has advanced with the development of astronomy and space exploration, including observations from space telescopes and spacecraft.
The Sun's activity, particularly solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can have profound effects on Earth's magnetosphere, ionosphere, and exosphere, potentially disrupting radio communications, power grids, and satellites. This field of study is known as space weather.
Future[edit]
The Sun is about 4.6 billion years old and has used up about half of the hydrogen in its core. It will continue to burn hydrogen in its core for another 5 billion years, after which it will expand into a red giant and eventually shed its outer layers, leaving behind a white dwarf.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
