Solar irradiance
Solar Irradiance[edit]

Solar irradiance is the power per unit area received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. It is measured in watts per square meter (W/m²) in SI units. Solar irradiance is an important factor in the study of climate, solar energy, and atmospheric science.
Types of Solar Irradiance[edit]
Solar irradiance can be categorized into different types based on the path it takes to reach the Earth's surface:
- Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI): This is the solar radiation received per unit area by a surface that is always held perpendicular (or normal) to the rays that come in a straight line from the direction of the sun. It is important for concentrating solar power systems.
- Diffuse Horizontal Irradiance (DHI): This is the solar radiation received from the sun after its direction has been changed by scattering by the atmosphere. It is measured on a horizontal surface.
- Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI): This is the total amount of shortwave radiation received from above by a horizontal surface. It is the sum of direct and diffuse solar radiation.
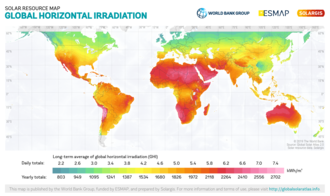
Measurement of Solar Irradiance[edit]
Solar irradiance is measured using instruments such as pyranometers and pyrheliometers.
- A pyranometer measures global solar irradiance on a planar surface and is used to measure both direct and diffuse solar radiation.
- A pyrheliometer measures direct beam solar irradiance and is used to measure DNI.


Factors Affecting Solar Irradiance[edit]
Several factors affect the amount of solar irradiance received at a given location on Earth:
- Solar zenith angle: The angle between the sun and the vertical directly affects the intensity of solar radiation. The smaller the angle, the more intense the radiation.
- Atmospheric conditions: Clouds, dust, and pollution can scatter and absorb solar radiation, reducing the amount of solar irradiance reaching the surface.
- Earth's orbit and axial tilt: The Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years, affecting solar irradiance.
Solar Spectrum[edit]
The solar spectrum is the distribution of solar radiation as a function of wavelength. It includes ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation. The solar spectrum is crucial for understanding the energy balance of the Earth and the design of solar energy systems.
Applications of Solar Irradiance[edit]
Solar irradiance data is essential for various applications, including:
- Designing and optimizing solar power systems.
- Studying and modeling climate change.
- Understanding and predicting weather patterns.
Related Pages[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
Linkedin_Shiny_Icon ![]() YouTube_icon_(2011-2013)
Error creating thumbnail:
YouTube_icon_(2011-2013)
Error creating thumbnail:
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian