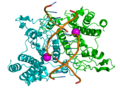
Restriction enzyme
Restriction enzymes, also known as restriction endonucleases, are enzymes that cut DNA at or near specific recognition sequences known as restriction sites. These enzymes are essential tools in molecular biology and genetic engineering, enabling scientists to cut DNA into smaller fragments, which can then be easily studied or manipulated. The discovery of restriction enzymes was pivotal in the development of recombinant DNA technology, leading to the birth of modern biotechnology.
History[edit]
The existence of restriction enzymes was first discovered in the 1950s through the work of scientists studying the phenomenon of bacteriophage resistance in bacteria. It was observed that certain bacteria could "restrict" the growth of bacteriophage by cutting its DNA. The first restriction enzyme, HindII, was isolated and characterized in the early 1970s by Hamilton O. Smith and Daniel Nathans, an achievement for which they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1978.
Types of Restriction Enzymes[edit]
Restriction enzymes are categorized into three main types, based on their structure, specificity, and requirements for cleavage:
- Type I enzymes cut DNA at sites that are distant from their recognition sequences and require ATP for activity.
- Type II enzymes are the most widely used in molecular biology. They cut DNA within or at short specific distances from their recognition sites and do not require ATP.
- Type III enzymes cut DNA a short distance away from their recognition sites and require ATP, but unlike Type I enzymes, their recognition and cleavage sites are closely linked.
Mechanism of Action[edit]
Restriction enzymes recognize specific, short sequences of DNA, typically 4-8 base pairs in length, and cleave the DNA strand at or near these sites. The recognition sequences are generally palindromic, meaning the sequence reads the same in the opposite direction on the complementary strand. Upon binding to their recognition sequence, restriction enzymes make two cuts, one through each strand of the DNA double helix, resulting in the fragmentation of the DNA.
Applications[edit]
Restriction enzymes have numerous applications in molecular biology, including:
- DNA cloning: Cutting DNA into fragments to be inserted into plasmids or other vectors for replication and expression in host organisms.
- Genetic engineering: Facilitating the insertion or removal of genetic material to modify the genome of an organism.
- Molecular cloning: Enabling the assembly of recombinant DNA molecules that can be propagated in a host organism.
- Genome mapping: Cutting genomes into smaller fragments that can be separated and analyzed to construct genetic maps.
Limitations and Considerations[edit]
While restriction enzymes are powerful tools, their use comes with certain limitations. The availability of a specific recognition site within the target DNA is a prerequisite for the use of a particular enzyme, which may not always be present. Additionally, the generation of compatible ends (cohesive or blunt ends) between DNA fragments for ligation can be a challenge, requiring careful selection of enzymes or additional processing of DNA ends.
See Also[edit]

This article is a molecular biology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Restriction_enzyme[edit]
-
GelDoc DNA gel electrophoresis photograph stained with ethidium bromide
-
EcoRV Restriction Site
-
EcoRI restriction enzyme recognition site
-
SmaI restriction enzyme recognition site
-
1QPS
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian