Refrigerator


File:Theater commercial, electric refrigerator, 1926.ogv


Appliance for preserving food at low temperatures
Refrigerator
{{This appliance-related article is a stub.}}
A refrigerator (colloquially fridge) is a common household appliance that consists of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic, or chemical) that transfers heat from its interior to its external environment so that its interior is cooled to a temperature below the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential food storage technique in developed countries. Lower temperatures in a confined volume lower the reproduction rate of bacteria, so the refrigerator reduces the rate of spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. Optimum temperature range for perishable food storage is 3 to 5 °C (37 to 41 °F). A similar device that maintains a temperature below the freezing point of water is called a freezer.
History[edit]
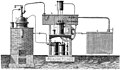
The first known artificial refrigeration was demonstrated by William Cullen at the University of Glasgow in 1748. The first practical vapor-compression refrigeration system was built by Jacob Perkins in 1834. The first commercial ice-making machine was invented in 1854, and the first refrigerator for domestic use was invented in 1913.
Types[edit]
Refrigerators come in various types, including:
- Top-freezer refrigerator
- Bottom-freezer refrigerator
- Side-by-side refrigerator
- French door refrigerator
- Compact refrigerator
- Wine refrigerator
Components[edit]
A typical refrigerator consists of the following components:
Refrigerants[edit]
Refrigerants are substances used in a heat cycle to transfer heat from one area and remove it to another. Common refrigerants include:
Energy Efficiency[edit]
Modern refrigerators are designed to be energy efficient. The Energy Star program certifies appliances that meet certain energy efficiency criteria. Features such as inverter compressors and improved insulation contribute to lower energy consumption.
Maintenance[edit]
Regular maintenance of a refrigerator includes:
- Cleaning the condenser coils
- Checking the door seals
- Defrosting the freezer
- Replacing the water filter (if applicable)
Environmental Impact[edit]
Refrigerators have an environmental impact due to the refrigerants used and the energy consumed. Older refrigerants like CFCs and HCFCs have been phased out due to their ozone-depleting properties. Modern refrigerants are designed to be more environmentally friendly.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External links[edit]
Refrigerator[edit]
-
Samsung Refrigerator
-
Open Refrigerator with Food at Night
-
Theater Commercial, Electric Refrigerator, 1926
-
Gorrie Ice Machine
-
Appareil Carré
-
Linde Cycle 1895-1903 Patent Cryo
-
French Refrigerator Plant Increases its Productivity
-
DOMELRE Refrigerator c. 1914
-
Monitor Refrigerator
-
Refrigerator Cycle
-
Introduction to the Process and Components of a Conventional Refrigerator
-
Refrigerator Cycle
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian