Pome
Pome is a type of fruit produced by flowering plants in the subtribe Malinae of the family Rosaceae. The best-known examples of pomes are apples and pears, although there are also other types of fruits that fall into this category.
Definition[edit]
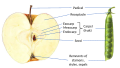
A pome is a type of fruit that is characterized by a structure in which the seeds are surrounded by a tough, central core, and the edible portion of the fruit is derived from the receptacle tissue, rather than from the ovary tissue as in most other fruits. The word "pome" comes from the Latin word pomum, which means "fruit".
Characteristics[edit]
Pomes are typically round or oval in shape and can vary in size from small (like a cherry) to large (like a grapefruit). The skin of a pome is often tough and waxy, and the flesh is usually juicy and sweet, although it can sometimes be tart or even bitter. The central core of a pome contains the seeds, which are often hard and inedible.
Examples[edit]
The most well-known examples of pomes are apples and pears. However, other fruits that are classified as pomes include quinces, loquats, and medlars. Some types of berries, such as hawthorn berries and rowan berries, are also considered pomes.
Cultivation[edit]
Pomes are cultivated in various parts of the world, with apples and pears being the most widely grown. They are typically grown in temperate climates, as they require a period of cold dormancy in order to produce fruit. Pomes are often grown in orchards, where they are pruned and trained to optimize fruit production.
Uses[edit]
Pomes are used in a variety of culinary applications. They can be eaten fresh, cooked, or preserved. They are also used to make beverages, such as cider and perry, and are often used in baking and dessert recipes.
Health Benefits[edit]
Pomes are rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and potassium. They are also a good source of dietary fiber, which can aid in digestion and help to lower cholesterol levels. Some studies have suggested that consuming pomes may have additional health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer.
-
Anatomy comparison of an apple and a peapod
-
Image of Mespilus germanica
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian