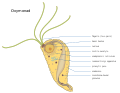
Oxymonad
Oxymonad is a group of flagellate protozoa that are primarily known for their role in the digestive systems of termites and cockroaches. These single-celled organisms are part of the phylum Oxymonadida, which is characterized by the absence of mitochondria, making them unique among eukaryotes. Oxymonads reside in the hindgut of their hosts, where they play a crucial role in the breakdown of cellulose and other complex polysaccharides, facilitating the digestion process for their insect hosts.
Characteristics[edit]
Oxymonads are distinguished by several key features:
- Lack of Mitochondria: Unlike most eukaryotic cells, oxymonads do not possess mitochondria. This absence is thought to be an adaptation to their anaerobic (oxygen-free) living conditions.
- Multiple Flagella: They typically have four or more flagella, which are used for locomotion. Some species have a unique structure called the "rostellum," which is involved in attachment to the host's gut lining.
- Symbiotic Relationship: Oxymonads establish a mutualistic relationship with their hosts. They assist in breaking down cellulose, enabling the host to absorb nutrients, while the oxymonads benefit from a stable environment and constant food supply.
Ecology and Evolution[edit]
Oxymonads are found exclusively in the digestive systems of wood-eating insects, such as termites and cockroaches. This specialized niche has led to a highly adapted way of life, including the development of their cellulose-digesting capabilities. The evolutionary history of oxymonads is of particular interest because of their unique cellular characteristics and their role in the evolution of eukaryotic life without mitochondria.
Genetics and Molecular Biology[edit]
The study of oxymonad genetics and molecular biology is challenging due to their specialized habitat and the difficulty in culturing them outside their host. However, research has revealed that oxymonads possess a unique set of genes for cellulose digestion and energy metabolism that are distinct from those found in other organisms. This genetic makeup is key to their survival and symbiotic relationship with their hosts.
Importance in Research[edit]
Oxymonads are of interest to scientists for several reasons:
- Understanding Symbiosis: Studying oxymonads can provide insights into the complex symbiotic relationships between different species, including mechanisms of mutual benefit and adaptation.
- Evolutionary Biology: Their unique characteristics offer clues about the evolution of eukaryotic cells, particularly the loss of mitochondria and the adaptation to anaerobic environments.
- Biotechnology: The enzymes produced by oxymonads for cellulose digestion have potential applications in biofuel production and industrial processes.
See Also[edit]

Oxymonad[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian