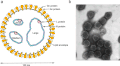
Orthobunyavirus
Orthobunyavirus is a genus of viruses within the family Bunyaviridae, which includes a wide range of viruses that are known to infect animals, including humans. Orthobunyaviruses are arthropod-borne viruses, meaning they are transmitted through the bites of insects such as mosquitoes and ticks. These viruses are responsible for a variety of diseases in humans and animals, ranging from mild febrile illnesses to severe encephalitis and hemorrhagic fevers.
Structure and Classification[edit]
Orthobunyaviruses are enveloped viruses with a segmented, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome. The genome is divided into three segments: large (L), medium (M), and small (S). The L segment encodes the viral polymerase, the M segment encodes the glycoproteins Gn and Gc which are involved in virus attachment and entry into host cells, and the S segment encodes the nucleocapsid protein and a nonstructural protein.
Orthobunyaviruses are classified into serogroups based on antigenic properties. Some of the well-known serogroups include the California serogroup, which includes La Crosse encephalitis virus; the Bunyamwera serogroup, which includes the Bunyamwera virus; and the Simbu serogroup, which includes the Oropouche virus.
Transmission and Epidemiology[edit]
Orthobunyaviruses are primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes, such as Aedes and Culex species, or ticks. The distribution of these viruses is closely related to the geographical distribution of their arthropod vectors. As a result, orthobunyavirus infections are more common in certain regions, particularly in tropical and subtropical areas where the climate is favorable for the vectors.
Animal hosts, including rodents, birds, and livestock, play a significant role in the maintenance and transmission of orthobunyaviruses. These animals can serve as reservoirs, harboring the virus without showing signs of illness, and contribute to the spread of the virus among vector populations.
Clinical Manifestations[edit]
The clinical manifestations of orthobunyavirus infections can vary widely, from asymptomatic infections to severe, life-threatening diseases. Common symptoms of orthobunyavirus infections in humans include fever, headache, fatigue, joint and muscle pain, and rash. In more severe cases, infections can lead to neurological complications such as encephalitis, or hemorrhagic fever, which is characterized by bleeding, organ failure, and shock.
The severity of the disease can depend on several factors, including the specific virus involved, the age and immune status of the infected individual, and the presence of underlying health conditions.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Diagnosis of orthobunyavirus infections is primarily based on clinical symptoms and is confirmed through laboratory tests, including virus isolation, serology, and molecular techniques such as reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
There is no specific antiviral treatment for orthobunyavirus infections. Management of the disease is supportive and focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for supportive care, including fluid management and treatment of secondary infections.
Prevention[edit]
Prevention of orthobunyavirus infections primarily involves controlling vector populations and minimizing exposure to vector bites. Measures include using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed. In some areas, vector control programs may include the use of insecticides and environmental management strategies to reduce vector populations.
Vaccines are not currently available for most orthobunyaviruses, although research is ongoing to develop effective vaccines for some of the more significant pathogens within this genus.
-
Peribunyavirus virion structure
-
Genome of Bunyamwera virus
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian