Orbivirus
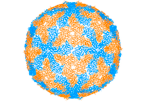


Orbivirus is a genus of viruses belonging to the family Reoviridae. Orbiviruses are arthropod-borne viruses, meaning they are transmitted by insects such as mosquitoes and ticks. This genus includes several important pathogens that affect animals and, in some cases, humans. The most well-known orbiviruses include Bluetongue virus, which affects ruminants like sheep and cattle, and African horse sickness virus, which is deadly to horses.
Structure and Classification[edit]
Orbiviruses are characterized by their double-stranded RNA genome, which is segmented into ten to twelve segments. This segmentation allows for a high degree of genetic reassortment, leading to a wide variety of strains and serotypes within the genus. The viruses are non-enveloped and possess an icosahedral capsid structure, which is typical of the Reoviridae family.
Transmission and Disease[edit]
The transmission of orbiviruses is primarily through blood-feeding arthropod vectors. The virus replicates in both the vector and the host, causing disease in the latter. The specific disease symptoms depend on the virus species and the host, ranging from mild to severe. In animals, symptoms can include fever, hemorrhagic conditions, edema, and, in severe cases, death.
Diagnosis and Control[edit]
Diagnosis of orbivirus infections is typically based on the detection of the virus or its RNA in blood samples, using techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Control measures are primarily focused on vector control to reduce transmission and vaccination of susceptible animals. For some orbiviruses, effective vaccines are available and widely used in endemic areas.
Research and Importance[edit]
Research on orbiviruses is crucial for understanding their biology, epidemiology, and interaction with hosts and vectors. This knowledge is essential for developing effective control strategies and vaccines. Orbiviruses are of significant concern in veterinary medicine due to their impact on livestock health and the economic losses they can cause. There is also interest in their potential threat to human health, although direct infections in humans are rare.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian