Obesity in the Pacific

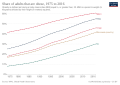
Obesity in the Pacific refers to the high prevalence of obesity among the populations of the Pacific Islands, which has become a significant public health concern. This phenomenon is particularly notable in regions such as Polynesia, Micronesia, and Melanesia, where rates of obesity and related health conditions rank among the highest globally.
Causes[edit]
The causes of obesity in the Pacific are multifaceted, involving a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and societal factors. One major factor is the transition from traditional diets, which were high in complex carbohydrates and low in fat, to more Westernized diets that are high in sugar, fat, and processed foods. This dietary shift has been exacerbated by globalization and the increased availability of processed foods. Additionally, a decline in physical activity due to urbanization and changes in lifestyle has contributed to the rising obesity rates.
Health Implications[edit]
Obesity in the Pacific has significant health implications, including an increased risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain forms of cancer. The high prevalence of obesity also places a strain on healthcare systems in these regions, many of which are already under-resourced.
Prevention and Intervention[edit]
Efforts to address obesity in the Pacific involve a combination of public health initiatives aimed at promoting healthier diets and increasing physical activity. These include policies to reduce the importation and consumption of unhealthy foods, the promotion of traditional diets, and the implementation of community-based physical activity programs. Education and awareness campaigns are also critical in changing public perceptions and behaviors related to diet and lifestyle.
Cultural Factors[edit]
Cultural factors play a significant role in the obesity epidemic in the Pacific. In many Pacific Island cultures, larger body sizes are traditionally associated with beauty, wealth, and social status. This cultural preference can pose challenges to obesity prevention and intervention efforts.
Conclusion[edit]
Obesity in the Pacific is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management and prevention. Addressing this epidemic will involve concerted efforts from governments, health organizations, communities, and individuals to promote healthier lifestyles while respecting cultural values and traditions.
Obesity in the Pacific[edit]
-
Participants of a walk against Diabetes and for general fitness around Nauru airport
-
Young Nauruan people
-
Obesity in the Pacific
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian