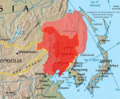
Manchuria
Manchuria is a region in East Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria can either refer to a region falling entirely within China, or a larger region today divided between Northeast China and Russia's Far East. The Chinese definition refers to the three provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning, but the international definition also includes the eastern part of Inner Mongolia.
History[edit]
Manchuria has a long history of conquest and power struggles among various ethnic groups, including the Mohe, Jurchen, Mongols, and Manchu. The region was the homeland of the Manchu people who established the Qing dynasty, which ruled China from 1644 to 1912.
Geography[edit]
Manchuria is a region defined by its geography, with high mountains forming its eastern and southern boundaries. The region is also known for its vast forests and rich mineral resources.
Economy[edit]
Manchuria's economy is heavily dependent on its vast natural resources. The region is one of the world's largest suppliers of raw materials, including coal, oil, and iron ore. It also has a significant agricultural sector, producing crops such as soybeans, corn, and wheat.
Culture[edit]
Manchuria is home to a diverse range of cultures, with influences from the Manchu, Han Chinese, Korean, Mongol, and Russian cultures. The region is known for its traditional music, dance, and art, as well as its unique cuisine.
See also[edit]
|
|
|
-
Manchuria
-
Amurrivermap
-
John-Tallis-1851-Tibet-Mongolia-and-Manchuria-NE
-
EB1911 Manchuria
-
Manchukuo Railmap
-
Ming divisions
-
The Americana - a universal reference library
-
Climate Map for Manchuria-Northeast China
-
China Railways passenger train K1452 on Binsui railway
-
Ussuriysk Stone Tortoise
-
Three Kingdoms of Korea Map
-
Yuan dynasty and Manchuria
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian