Indirect calorimetry
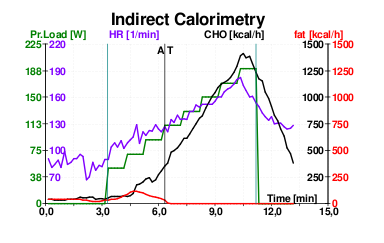
Indirect calorimetry is a method used to estimate the oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production rates of an organism, which are indicative of its metabolic rate. This technique is based on the principle that the amount of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced can be used to calculate energy expenditure, assuming a steady state of gas exchange. Indirect calorimetry is widely used in various fields such as nutrition, exercise physiology, and critical care medicine to assess the metabolic status of individuals.
Principles[edit]
The fundamental principle behind indirect calorimetry is the measurement of oxygen consumption (VO2) and carbon dioxide production (VCO2). These measurements are used to calculate the respiratory quotient (RQ), which is the ratio of VCO2 to VO2. The RQ provides information about the substrate being metabolized for energy, with values typically ranging from 0.7 (indicating fat oxidation) to 1.0 (indicating carbohydrate oxidation).
Applications[edit]
Indirect calorimetry has a wide range of applications. In nutrition, it is used to assess the metabolic rate and thus tailor dietary interventions for weight management. In exercise physiology, it helps in evaluating an athlete's aerobic capacity and endurance. In critical care medicine, it is utilized to optimize nutritional support for critically ill patients, ensuring that their energy requirements are met without overfeeding or underfeeding.
Procedure[edit]
The procedure for conducting indirect calorimetry involves the use of a metabolic cart, which measures the volumes of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced. The subject typically breathes into a mouthpiece or wears a mask connected to the metabolic cart, which captures and analyzes the exhaled gases. The data collected is then used to calculate the metabolic rate using standard equations.
Advantages and Limitations[edit]
One of the main advantages of indirect calorimetry is its non-invasive nature, making it a safe and relatively easy method to assess metabolic rate. However, the accuracy of the measurements can be affected by various factors, including the type of equipment used, the subject's compliance with the breathing apparatus, and the steady state of gas exchange.
Conclusion[edit]
Indirect calorimetry is a valuable tool in assessing the metabolic rate and understanding the energy expenditure of individuals. Its applications across various fields highlight its importance in both research and clinical settings. Despite its limitations, it remains a widely used method for evaluating metabolic health and guiding nutritional and exercise interventions.
Indirect Calorimetry[edit]
-
Indirect calorimetry laboratory with canopy hood
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian

