Francia






Francia
Francia, also known as the Frankish Empire or Frankish Kingdom, was a collection of Germanic tribes, primarily the Franks, that established a significant political and cultural entity in Western Europe during the early Middle Ages. The term "Francia" is derived from the Latin name for the land of the Franks.
History[edit]
The history of Francia can be divided into several key periods:
Merovingian Dynasty[edit]
The Merovingian dynasty was the first ruling dynasty of Francia, founded by Clovis I in the late 5th century. Clovis united the Frankish tribes under one ruler and converted to Christianity, which helped to solidify his power and establish a relationship with the Roman Catholic Church.
Carolingian Dynasty[edit]
The Carolingian dynasty succeeded the Merovingians in the 8th century. The most notable ruler of this dynasty was Charlemagne, who expanded the Frankish Empire to its greatest extent and was crowned Holy Roman Emperor in 800 AD. The Carolingian Renaissance was a period of cultural and intellectual revival that occurred during Charlemagne's reign.
Division and Decline[edit]
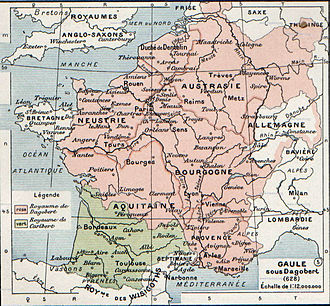
After the death of Charlemagne, the empire was divided among his grandsons through the Treaty of Verdun in 843 AD. This division led to the formation of three separate kingdoms: West Francia, East Francia, and Middle Francia. The fragmentation of the empire continued, eventually leading to the formation of modern European states such as France and Germany.
Geography[edit]
Francia covered a vast area that included parts of modern-day France, Germany, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Switzerland. The Rhine and Seine rivers were significant geographical features within the empire.
Culture[edit]
The culture of Francia was a blend of Roman, Germanic, and Christian influences. The Frankish legal system, known as Salic law, was one of the earliest codified legal systems in Europe. The Carolingian Renaissance saw a revival of art, literature, and learning, heavily influenced by classical Roman and Christian traditions.
Religion[edit]
Christianity played a central role in the Frankish Empire. The conversion of Clovis I to Christianity marked the beginning of a close relationship between the Frankish rulers and the Roman Catholic Church. Monasteries and churches were centers of learning and culture during this period.
Legacy[edit]
The legacy of Francia is evident in the formation of modern European states and the spread of Christianity throughout Europe. The Carolingian Renaissance laid the groundwork for the later cultural and intellectual developments of the Middle Ages.
Related Pages[edit]
- Clovis I
- Charlemagne
- Merovingian dynasty
- Carolingian dynasty
- Treaty of Verdun
- Holy Roman Empire
- Salic law
- Carolingian Renaissance
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
