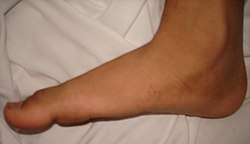
Flat feet

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Flat feet | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Pes planus, fallen arches |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Foot pain, knee pain, ankle pain |
| Complications | Plantar fasciitis, shin splints, bunions |
| Onset | Can be present from birth or develop over time |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetics, injury, arthritis, obesity |
| Risks | Obesity, diabetes, aging, pregnancy |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, X-ray, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Tarsal coalition, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Orthotics, physical therapy, surgery |
| Medication | Pain relievers |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Flat feet, also known as pes planus or fallen arches, is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. This condition can occur when the arches don't develop during childhood or they collapse under weight over time.


Classification[edit]
Flat feet can be classified into two types:

- Flexible flat feet: The arches on the feet are visible when the person is sitting or standing on tiptoes, but disappear when standing normally.
- Rigid flat feet: The arch is not visible regardless of whether the person is sitting, standing on tiptoes, or standing normally<ref>
Flatfeet(link). {{{website}}}. Harvard Health.
</ref>.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
In many instances, flat feet do not cause any problems. However, potential signs and symptoms may include:
- Feet tire easily
- Painful or achy feet, particularly in the areas of the arches and heels
- Swelling along the inside of the ankle
- Difficulty with foot movement, such as standing on the toes<ref>
Flatfeet(link). {{{website}}}. Mayo Clinic.
</ref>.
Causes[edit]
Flat feet can be congenital, meaning people are born with the condition. In some cases, flat feet develop over time due to aging, obesity, or pregnancy. Other potential causes include:
- Injuries or overuse of the feet
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Dysfunction, rupture, or damage to the posterior tibial tendon
- Nervous system or muscle diseases, such as cerebral palsy, spina bifida, or muscular dystrophy<ref>
What Are Fallen Arches?(link). {{{website}}}. WebMD.
</ref>.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider and may include observing the feet and the individual walking. The provider may also examine the wear pattern on the person's shoes. Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be used for a comprehensive evaluation<ref>
Pes Planus(link). {{{website}}}. NCBI.
</ref>.
Treatment[edit]
In cases where flat feet cause pain or other symptoms, treatment options may include:
- Orthotic devices or insoles: These are designed to support the arch of the foot.
- Stretching exercises: Certain exercises may help reduce symptoms.
- Supportive shoes: Shoes that have good arch support and avoid tight or high-heeled shoes.
- Physical therapy: Specific exercises can strengthen the feet and ankles.
- Surgery: In severe cases where non-surgical treatments haven't been successful<ref>
Flatfeet(link). {{{website}}}. Mayo Clinic.
</ref>.
Prognosis[edit]
While flat feet can cause pain and other issues, it's a common and typically non-serious condition. Many people with flat feet lead perfectly healthy lives. For those with persistent pain, solutions are available.
Prevention[edit]
While some causes of flat feet, such as genetic factors or aging, cannot be prevented, some preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing painful flat feet:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can put additional stress on the feet.
- Regular exercise: It can help keep joints more flexible and strengthen the muscles supporting the foot.
- Proper footwear: Wearing shoes with good arch support and a low heel can help.
- Limit wearing high heels: They can put stress on the arches<ref>
Flatfeet(link). {{{website}}}. Healthline.
</ref>.
Complications[edit]
Flat feet can occasionally contribute to problems in your ankles and knees because it can alter the alignment of your legs. If you aren't experiencing any pain, no treatment is typically necessary for flat feet. However, if flat feet are causing pain, it's important to seek treatment to alleviate discomfort and avoid potential complications such as:
- Shin splints
- Stress fractures
- Bunions and hammertoes
- Pain in the lower back, hips or knees<ref>
What Are Fallen Arches?(link). {{{website}}}. WebMD.
</ref>.
Society and Culture[edit]
Flat feet are common in both children and adults, and they can occur in people of all fitness levels and backgrounds. Many athletes with flat feet have successful careers in sports. The key to a healthy lifestyle, even with flat feet, is proper care and treatment when symptoms occur.
External Links[edit]
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


